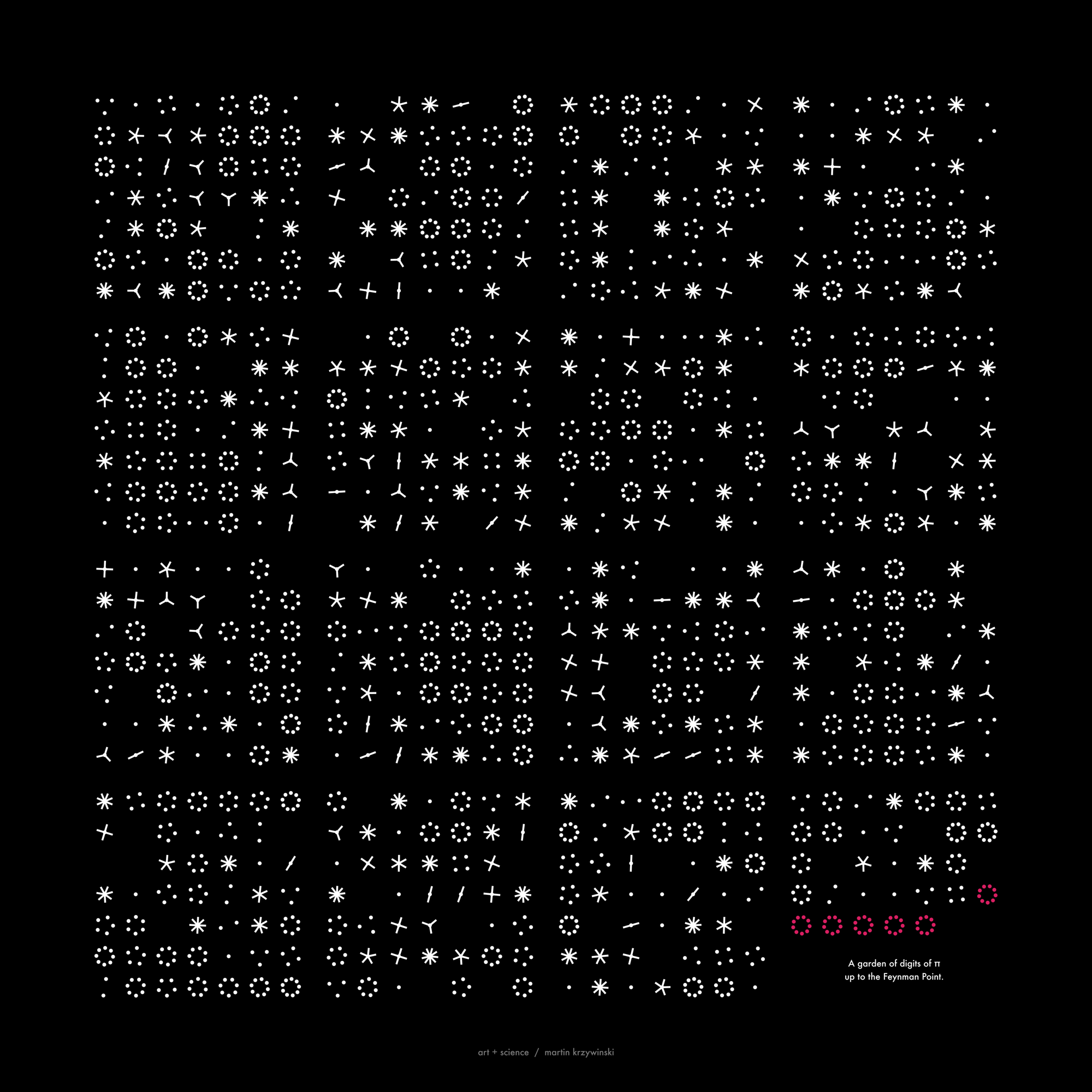
`\pi` Day 2017 Art Posters - Star charts and extinct animals and plants
On March 14th celebrate `\pi` Day. Hug `\pi`—find a way to do it.
For those who favour `\tau=2\pi` will have to postpone celebrations until July 26th. That's what you get for thinking that `\pi` is wrong. I sympathize with this position and have `\tau` day art too!
If you're not into details, you may opt to party on July 22nd, which is `\pi` approximation day (`\pi` ≈ 22/7). It's 20% more accurate that the official `\pi` day!
Finally, if you believe that `\pi = 3`, you should read why `\pi` is not equal to 3.
Caelum non animum mutant qui trans mare currunt.
—Horace
This year: creatures that don't exist, but once did, in the skies.
This year's `\pi` day song is Exploration by Karminsky Experience Inc. Why? Because "you never know what you'll find on an exploration".
create myths and contribute!
Want to contribute to the mythology behind the constellations in the `\pi` in the sky? Many already have a story, but others still need one. Please submit your stories!
This year I wanted to something more than visuals. Space is vast, so let's fill it with words.
I asked my good friend and poet, Paolo Marcazzan, to collaborate. I described the idea for the art—a universe of stars based on `\pi` and the extinct creatures that live within it—and asked him to find the matching words.
And they could not have been more perfect.
author's note
The poem situates the dark as a place for contention and ongoing confrontation. Whether in the recesses of space or heart, the poem probes the territory of distance, absence, uncertainty and muteness. It considers the relational as default positioning of existence (earthly, universal), and that which remains unmet within that context.
Life in its dimension of cross-grained, often broken linearity is juxtaposed with a quote form Dante that references instead his vision of sidereal circularity as the benign force that moves all things in the universe. For the earthbound, the questions and concerns remain those of identity, passage, escape from transiency, and slow tempering of hope.
Nasa to send our human genome discs to the Moon
We'd like to say a ‘cosmic hello’: mathematics, culture, palaeontology, art and science, and ... human genomes.



Comparing classifier performance with baselines
All animals are equal, but some animals are more equal than others. —George Orwell
This month, we will illustrate the importance of establishing a baseline performance level.
Baselines are typically generated independently for each dataset using very simple models. Their role is to set the minimum level of acceptable performance and help with comparing relative improvements in performance of other models.
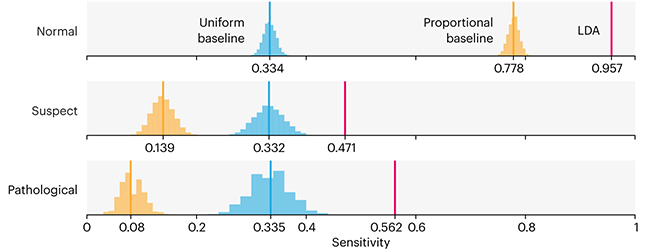
Unfortunately, baselines are often overlooked and, in the presence of a class imbalance5, must be established with care.
Megahed, F.M, Chen, Y-J., Jones-Farmer, A., Rigdon, S.E., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2024) Points of significance: Comparing classifier performance with baselines. Nat. Methods 20.
Happy 2024 π Day—
sunflowers ho!
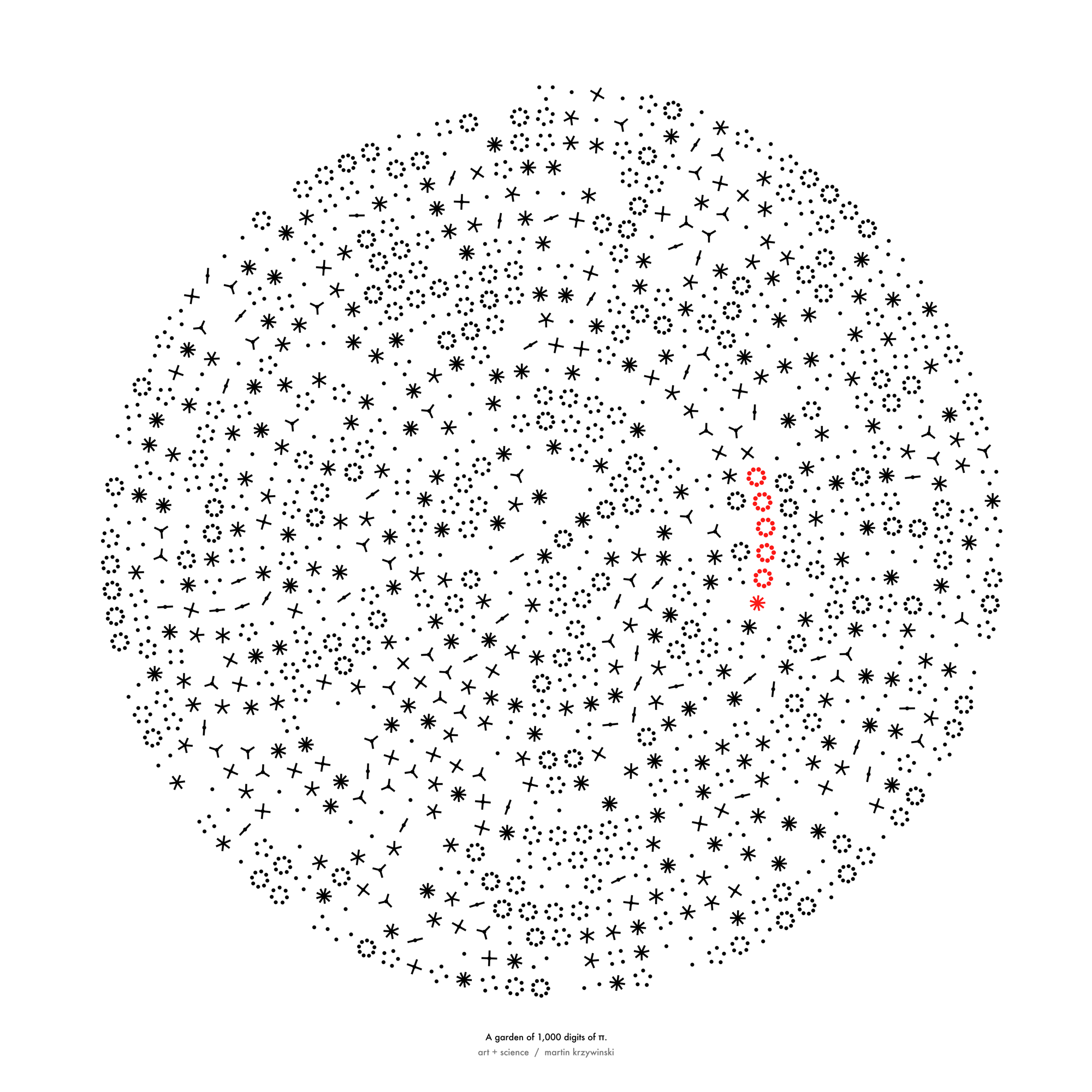
Celebrate π Day (March 14th) and dig into the digit garden. Let's grow something.
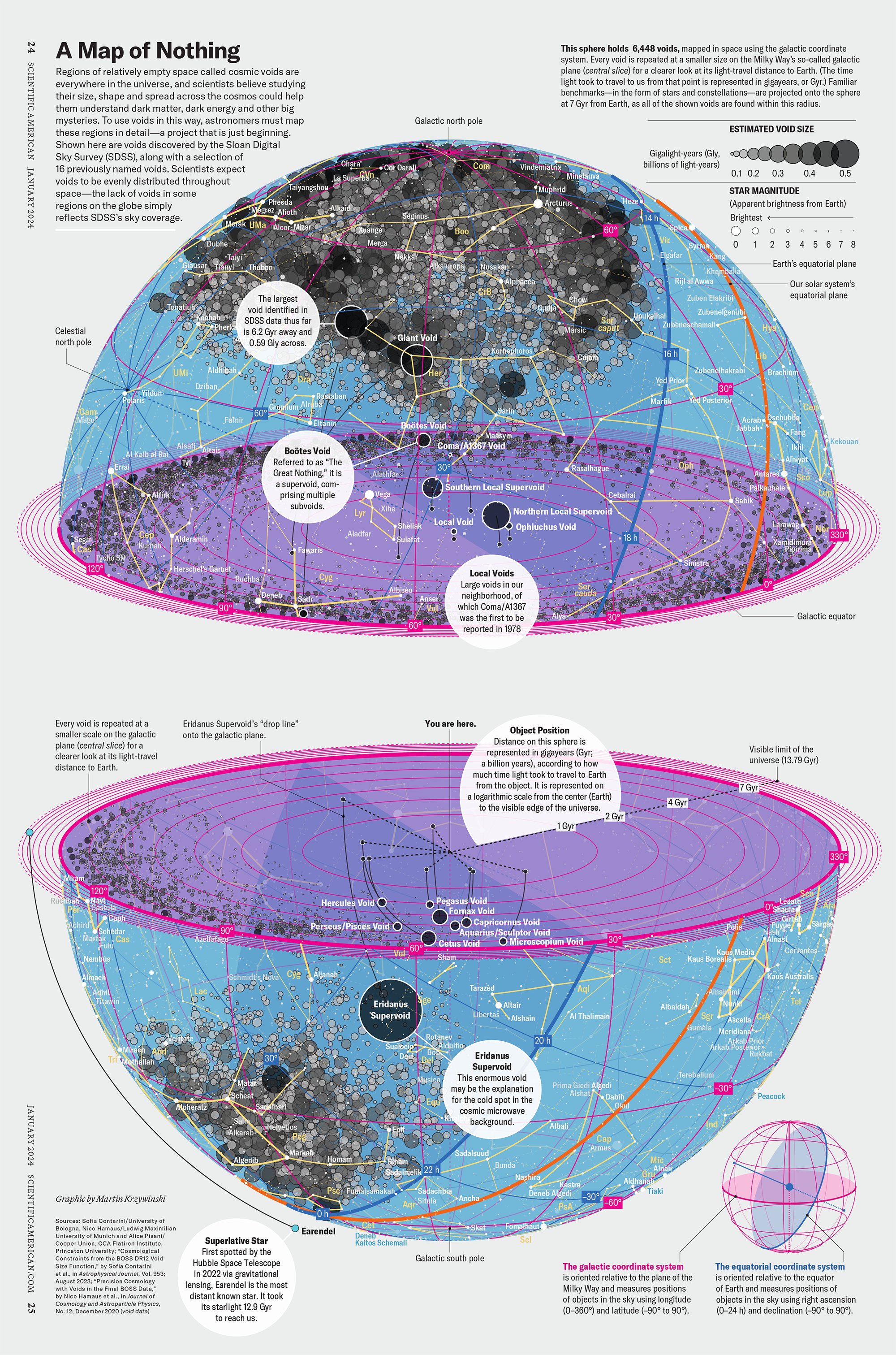
How Analyzing Cosmic Nothing Might Explain Everything
Huge empty areas of the universe called voids could help solve the greatest mysteries in the cosmos.
My graphic accompanying How Analyzing Cosmic Nothing Might Explain Everything in the January 2024 issue of Scientific American depicts the entire Universe in a two-page spread — full of nothing.
The graphic uses the latest data from SDSS 12 and is an update to my Superclusters and Voids poster.
Michael Lemonick (editor) explains on the graphic:
“Regions of relatively empty space called cosmic voids are everywhere in the universe, and scientists believe studying their size, shape and spread across the cosmos could help them understand dark matter, dark energy and other big mysteries.
To use voids in this way, astronomers must map these regions in detail—a project that is just beginning.
Shown here are voids discovered by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), along with a selection of 16 previously named voids. Scientists expect voids to be evenly distributed throughout space—the lack of voids in some regions on the globe simply reflects SDSS’s sky coverage.”
voids
Sofia Contarini, Alice Pisani, Nico Hamaus, Federico Marulli Lauro Moscardini & Marco Baldi (2023) Cosmological Constraints from the BOSS DR12 Void Size Function Astrophysical Journal 953:46.
Nico Hamaus, Alice Pisani, Jin-Ah Choi, Guilhem Lavaux, Benjamin D. Wandelt & Jochen Weller (2020) Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics 2020:023.
Sloan Digital Sky Survey Data Release 12
Alan MacRobert (Sky & Telescope), Paulina Rowicka/Martin Krzywinski (revisions & Microscopium)
Hoffleit & Warren Jr. (1991) The Bright Star Catalog, 5th Revised Edition (Preliminary Version).
H0 = 67.4 km/(Mpc·s), Ωm = 0.315, Ωv = 0.685. Planck collaboration Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters (2018).
constellation figures
stars
cosmology
Error in predictor variables
It is the mark of an educated mind to rest satisfied with the degree of precision that the nature of the subject admits and not to seek exactness where only an approximation is possible. —Aristotle
In regression, the predictors are (typically) assumed to have known values that are measured without error.
Practically, however, predictors are often measured with error. This has a profound (but predictable) effect on the estimates of relationships among variables – the so-called “error in variables” problem.
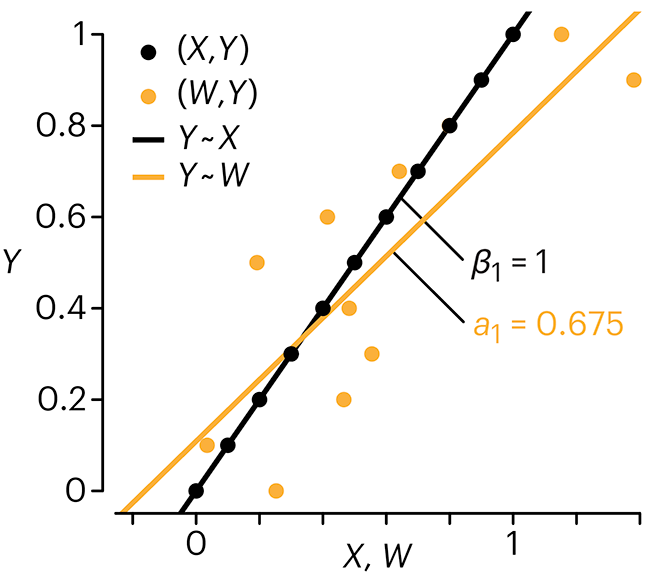
Error in measuring the predictors is often ignored. In this column, we discuss when ignoring this error is harmless and when it can lead to large bias that can leads us to miss important effects.
Altman, N. & Krzywinski, M. (2024) Points of significance: Error in predictor variables. Nat. Methods 20.
Background reading
Altman, N. & Krzywinski, M. (2015) Points of significance: Simple linear regression. Nat. Methods 12:999–1000.
Lever, J., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2016) Points of significance: Logistic regression. Nat. Methods 13:541–542 (2016).
Das, K., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2019) Points of significance: Quantile regression. Nat. Methods 16:451–452.
Convolutional neural networks
Nature uses only the longest threads to weave her patterns, so that each small piece of her fabric reveals the organization of the entire tapestry. – Richard Feynman
Following up on our Neural network primer column, this month we explore a different kind of network architecture: a convolutional network.
The convolutional network replaces the hidden layer of a fully connected network (FCN) with one or more filters (a kind of neuron that looks at the input within a narrow window).
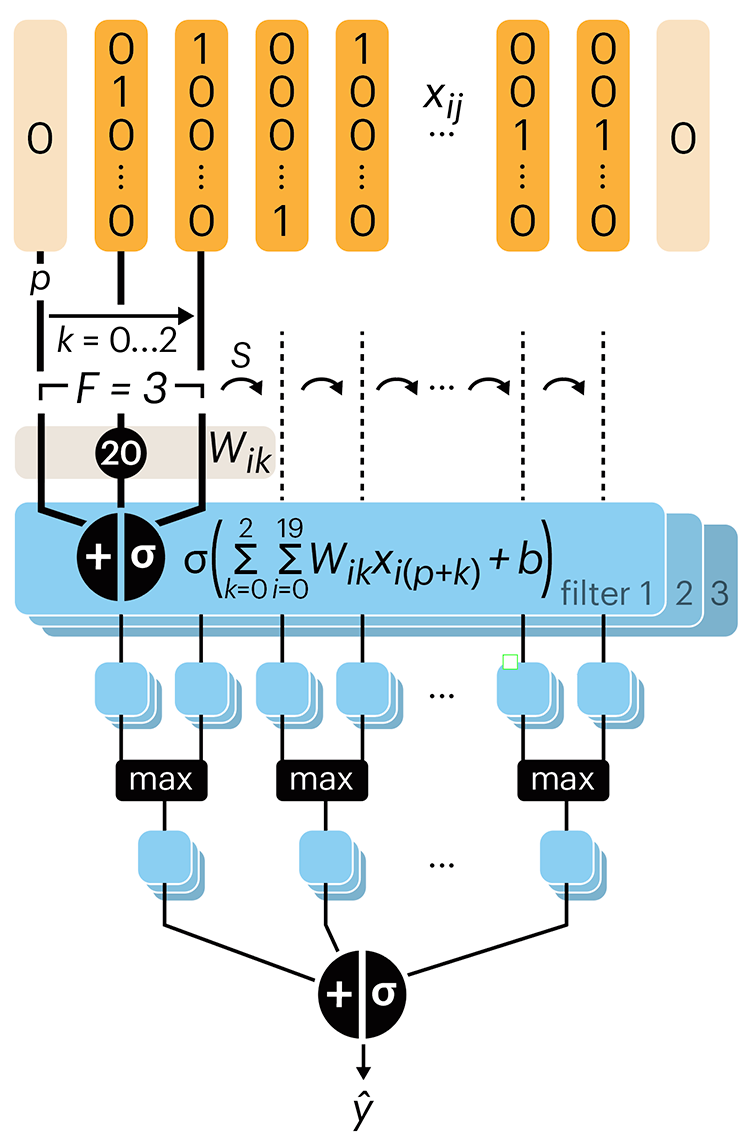
Even through convolutional networks have far fewer neurons that an FCN, they can perform substantially better for certain kinds of problems, such as sequence motif detection.
Derry, A., Krzywinski, M & Altman, N. (2023) Points of significance: Convolutional neural networks. Nature Methods 20:1269–1270.
Background reading
Derry, A., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2023) Points of significance: Neural network primer. Nature Methods 20:165–167.
Lever, J., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2016) Points of significance: Logistic regression. Nature Methods 13:541–542.