Alex — Internet's Former Most Popular Rat
contents
The rat genome sequencing project at the Baylor College of Medicine Human Genome Sequencing Centre is complete. The genome has been analyzed and published.
Here, I'd like to introduce you one of the faces of the project: Alex, the genomics rat idol.

Arguably, at one point Alex was the most popular rat on the internet. For the justification of this strong statement, read on.
Alex was born in May 2000. It's well known that a rat's cuteness reaches maximum at about 3-4 weeks. After this critical time, a pet store rat is less likely to be purchased and may be asked to act as snake food. In Alex's case, she was perilously close to her deadline. Luckily for her, we paid a ransom of $6.99 to the Noah's Ark pet shop in Vancouver. She was on her last cute leg.

From May 2000 Alex spent most of her time hoarding food pellets and riding on shoulders.

Alex liked to bite. And rats only bite hard — they don't nibble. Her contention for this unattractive behaviour was the uncanny similarity between a finger and a pellet of food.
Other than unpredictable bouts of biting (by far the most exciting aspect of her personality), Alex lacked other distinguishing characteristics.
Alex died of a seizure in late 2002. She was buried outside of the Museum of Anthropology. A ratty pair of underwear served as a burial shroud.
And I hope you got that last pun.
DOWNLOAD ALL PHOTOS — photos are for public use. Use, modification and distribution of these photos is unrestricted.
Despite my best efforts at meaningful work, this web page continues to be the most popular of all my online offerings, making for a somewhat embarrassing achievement.
Alex's images consistently show up first in Google's web search for 'rat', 'rat image' and image search for 'rat'. Excuse the very low quality screenshots.


Finally, Alex appears as the first entry in Google images for 'rat'.

Alex is neither without modesty nor public fame. Her first cover-ratgirl appearance was on the April 2004 issue of Genome Research.

More recently, she's appeared on the cover of Ethnologie Francaise (Jan-Mar 2009 issue). The topic of this issue was the relationship between animals and humans.

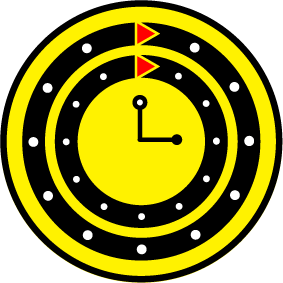
Propensity score weighting
The needs of the many outweigh the needs of the few. —Mr. Spock (Star Trek II)
This month, we explore a related and powerful technique to address bias: propensity score weighting (PSW), which applies weights to each subject instead of matching (or discarding) them.
Kurz, C.F., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2025) Points of significance: Propensity score weighting. Nat. Methods 22:1–3.
Happy 2025 π Day—
TTCAGT: a sequence of digits
Celebrate π Day (March 14th) and sequence digits like its 1999. Let's call some peaks.
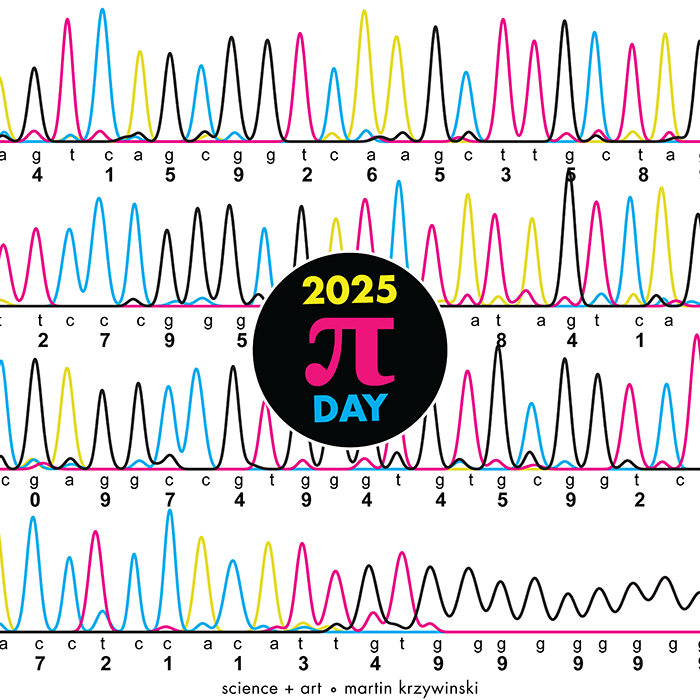
Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance
I don’t have good luck in the match points. —Rafael Nadal, Spanish tennis player
Points of Significance is an ongoing series of short articles about statistics in Nature Methods that started in 2013. Its aim is to provide clear explanations of essential concepts in statistics for a nonspecialist audience. The articles favor heuristic explanations and make extensive use of simulated examples and graphical explanations, while maintaining mathematical rigor.
Topics range from basic, but often misunderstood, such as uncertainty and P-values, to relatively advanced, but often neglected, such as the error-in-variables problem and the curse of dimensionality. More recent articles have focused on timely topics such as modeling of epidemics, machine learning, and neural networks.
In this article, we discuss the evolution of topics and details behind some of the story arcs, our approach to crafting statistical explanations and narratives, and our use of figures and numerical simulations as props for building understanding.
Altman, N. & Krzywinski, M. (2025) Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance. Annual Review of Statistics and Its Application 12:69–87.
Propensity score matching
I don’t have good luck in the match points. —Rafael Nadal, Spanish tennis player
In many experimental designs, we need to keep in mind the possibility of confounding variables, which may give rise to bias in the estimate of the treatment effect.
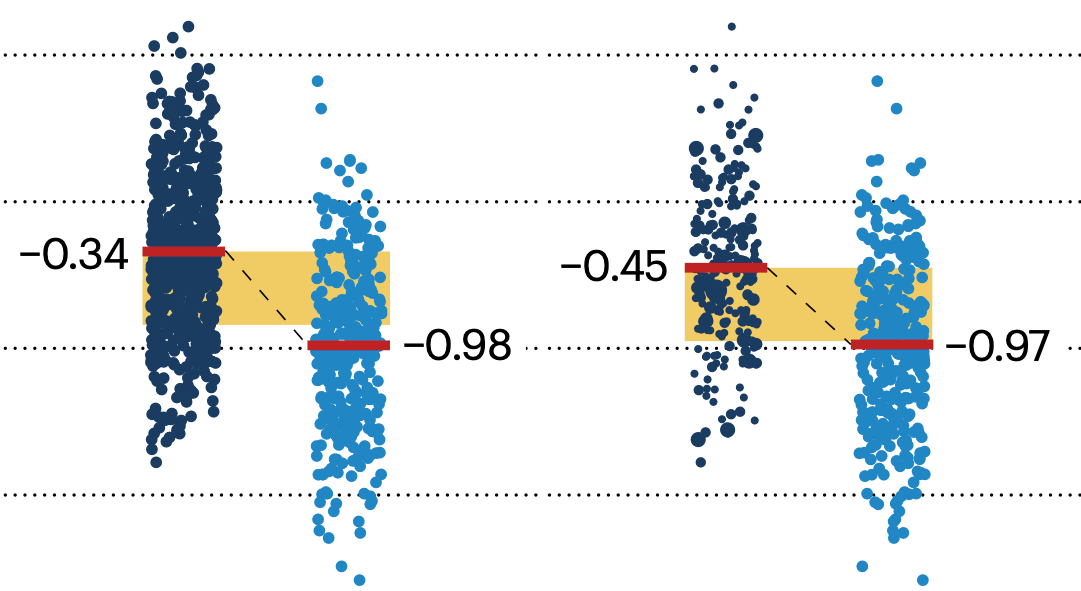
If the control and experimental groups aren't matched (or, roughly, similar enough), this bias can arise.
Sometimes this can be dealt with by randomizing, which on average can balance this effect out. When randomization is not possible, propensity score matching is an excellent strategy to match control and experimental groups.
Kurz, C.F., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2024) Points of significance: Propensity score matching. Nat. Methods 21:1770–1772.
Understanding p-values and significance
P-values combined with estimates of effect size are used to assess the importance of experimental results. However, their interpretation can be invalidated by selection bias when testing multiple hypotheses, fitting multiple models or even informally selecting results that seem interesting after observing the data.
We offer an introduction to principled uses of p-values (targeted at the non-specialist) and identify questionable practices to be avoided.
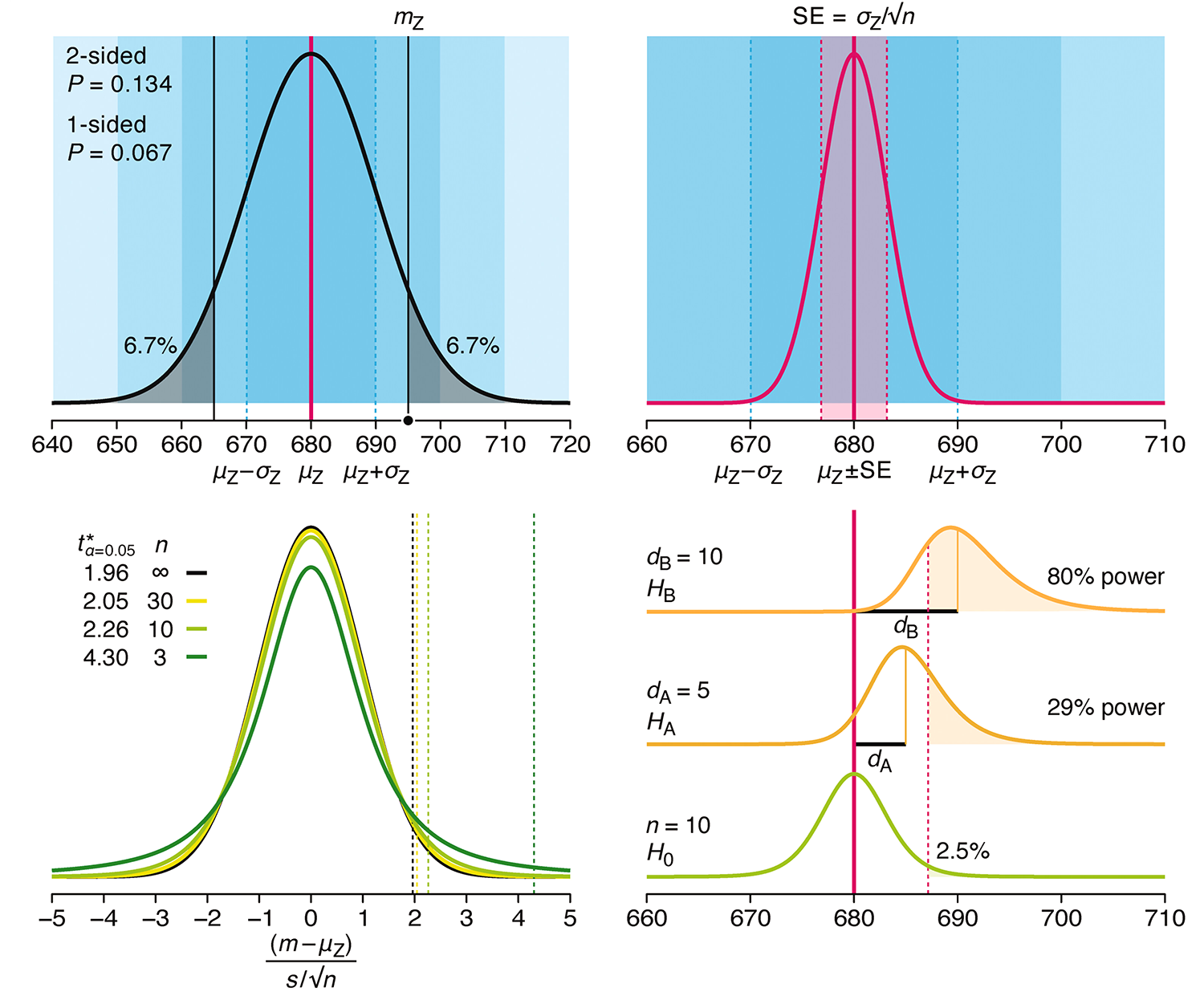
Altman, N. & Krzywinski, M. (2024) Understanding p-values and significance. Laboratory Animals 58:443–446.
Depicting variability and uncertainty using intervals and error bars
Variability is inherent in most biological systems due to differences among members of the population. Two types of variation are commonly observed in studies: differences among samples and the “error” in estimating a population parameter (e.g. mean) from a sample. While these concepts are fundamentally very different, the associated variation is often expressed using similar notation—an interval that represents a range of values with a lower and upper bound.
In this article we discuss how common intervals are used (and misused).
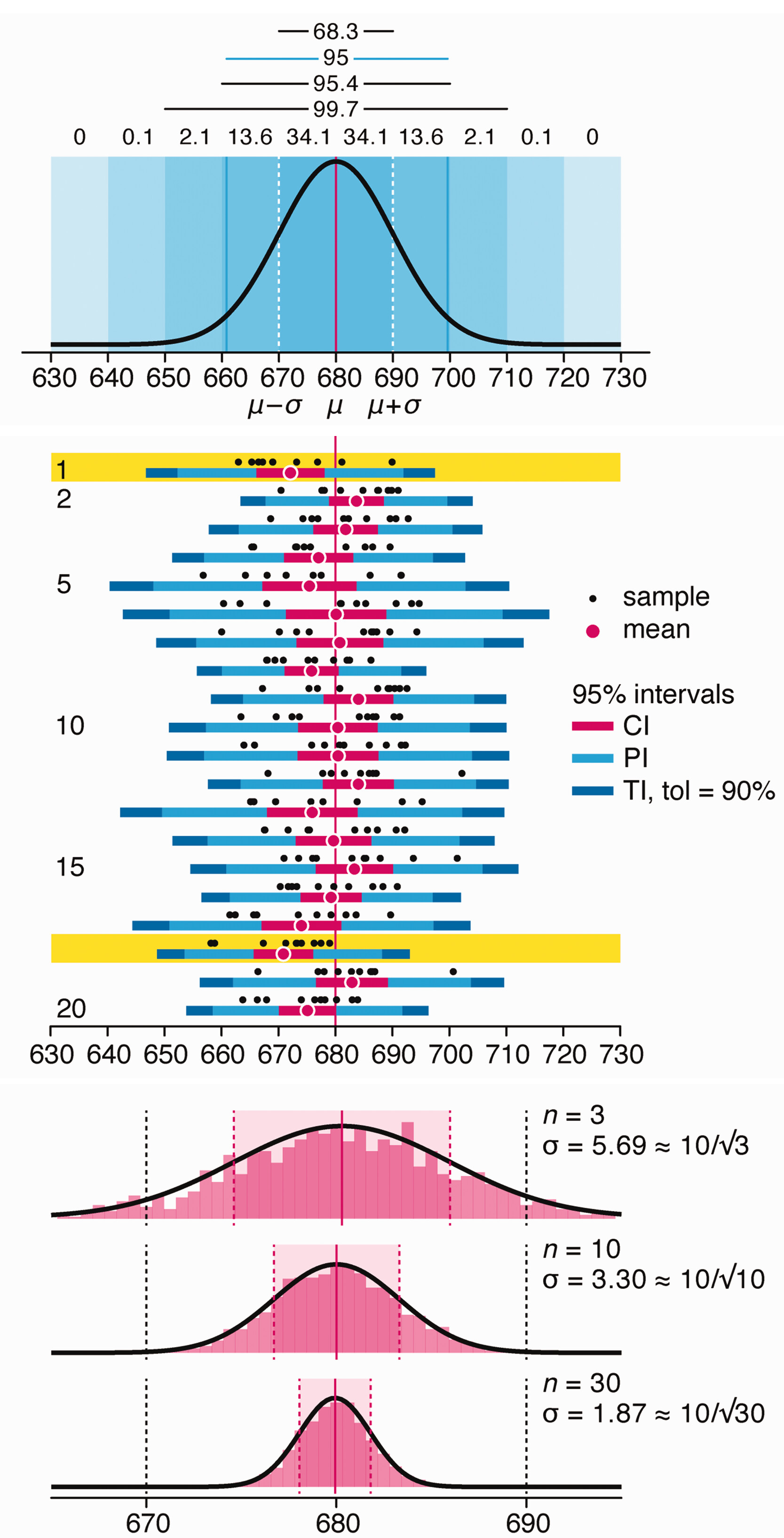
Altman, N. & Krzywinski, M. (2024) Depicting variability and uncertainty using intervals and error bars. Laboratory Animals 58:453–456.