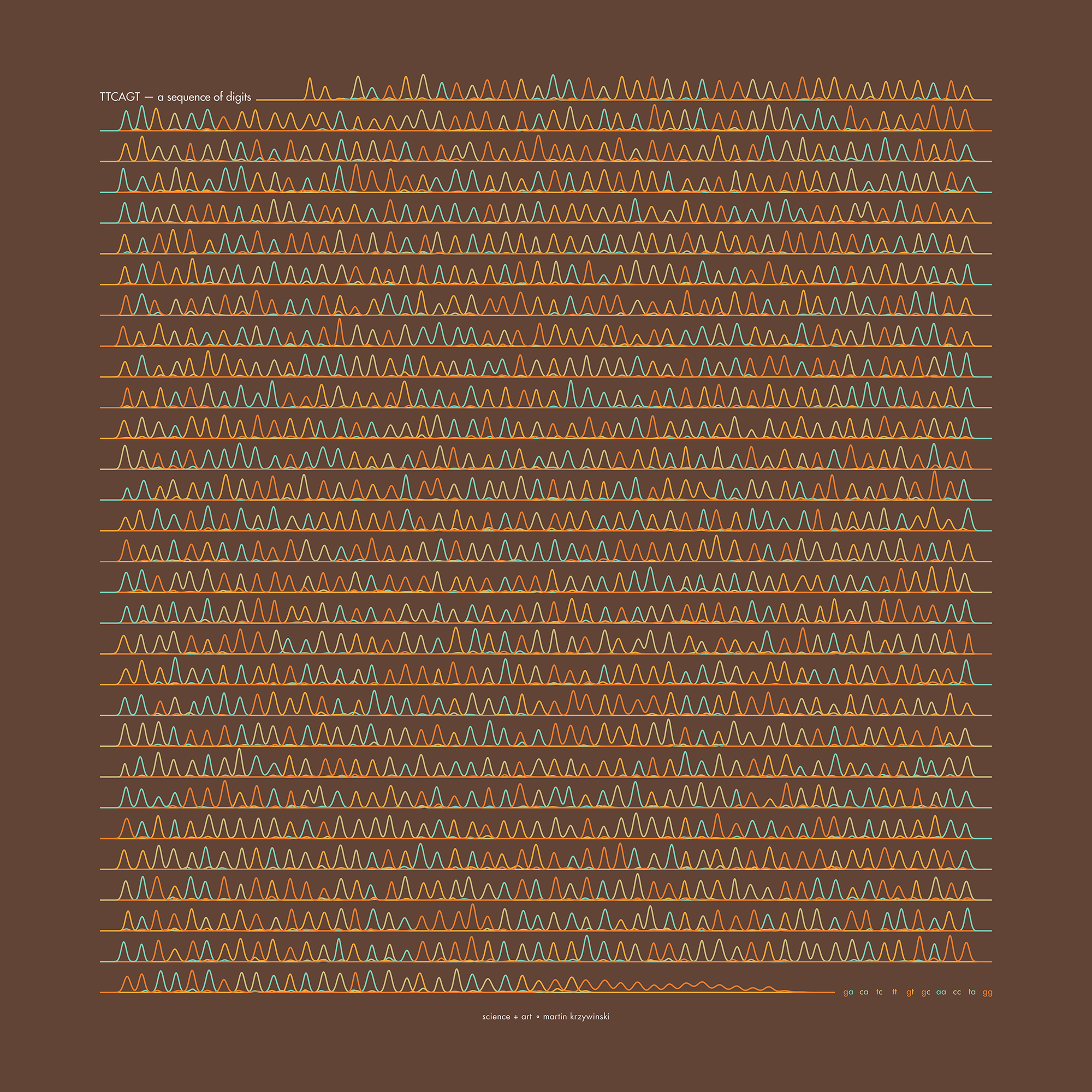 buy artwork
buy artwork
`\pi` Day 2015 Art Posters
On March 14th celebrate `\pi` Day. Hug `\pi`—find a way to do it.
For those who favour `\tau=2\pi` will have to postpone celebrations until July 26th. That's what you get for thinking that `\pi` is wrong. I sympathize with this position and have `\tau` day art too!
If you're not into details, you may opt to party on July 22nd, which is `\pi` approximation day (`\pi` ≈ 22/7). It's 20% more accurate that the official `\pi` day!
Finally, if you believe that `\pi = 3`, you should read why `\pi` is not equal to 3.
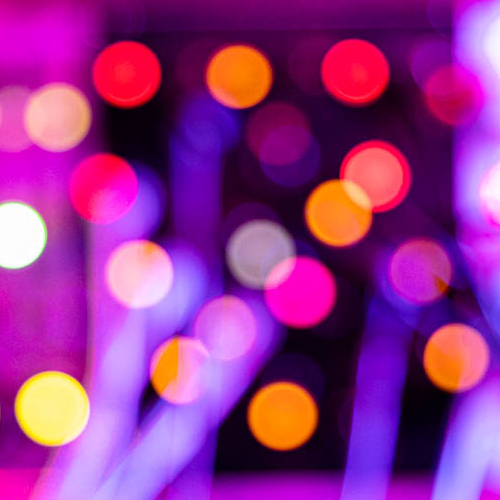
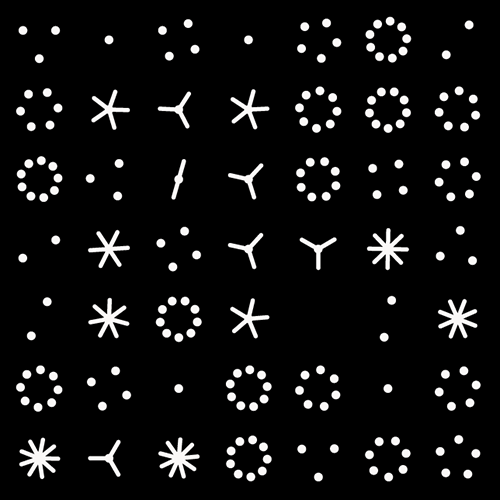
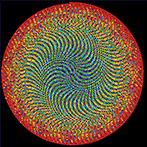
Not a circle in sight in the 2015 `\pi` day art. Try to figure out how up to 612,330 digits are encoded before reading about the method. `\pi`'s transcendental friends `\phi` and `e` are there too—golden and natural. Get it?
This year's `\pi` day is particularly special. The digits of time specify a precise time if the date is encoded in North American day-month-year convention: 3-14-15 9:26:53.
The art has been featured in Ana Swanson's Wonkblog article at the Washington Post—10 Stunning Images Show The Beauty Hidden in `\pi`.
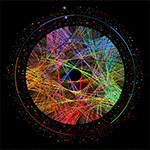
I find this image deeply beautiful and deeply troubling, and I’ll try to explain why. —Max Cooper
The 7-level tree map was used for the Transcendental Tree Map track on Max Cooper's Yearning for the Infinite album. The album is an “audio/visual rendering with our obsession with the unobtainable”.
The video for the track was a collaboration between myself and Nick Cobby. The music contains layered loops whose lengths are based on prime numbers—as the track plays, some loops individually come in and out of phase with others, forming a longer loop. The full set never synchronizes though.
The transcendental tree map encodes the first 20,244 digits of `\pi` = 3.1415...7012.
creating the video
The video constructs and then chaotically deconstructs a 7 level tree map of the digits of `\pi`. This map is shown below and is similar to other images I made for 2015 Pi Day, except that here the map is formatted for a 16:9 screen.
The video starts with an explicit construction of the map. This process begins with dividing the canvas with 3 vertical lines, which forms 4 rectangles. Each of the four rectangles formed by this process is divided with 1, 4, 1 and 5 horizontal lines, respectively. This forms 2 + 5 + 2 + 6 = 15 rectangles. Each of the 15 rectangles is divided by vertical lines according to the next 15 digits of Pi. This process repeats until we have performed the loop 7 times.
The division of each rectangle is not even—the positions of the lines are slightly jittered. This gives the map a more organic feel.
 buy artwork
buy artwork
The number of digits encoded in each loop is 1, 4, 15, 98, 548, 2,962 and 16,616. In total, 17,180 vertical and 3,064 horizontal lines are drawn and these form the backbone of the map.
The video is created by layering numerous animations of the construction of the map, in which the rate and order of line growth is varied. Blinking rectangles indicate that the lines for a digit have completed drawing.
Beyond Belief Campaign BRCA Art
Fuelled by philanthropy, findings into the workings of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes have led to groundbreaking research and lifesaving innovations to care for families facing cancer.
This set of 100 one-of-a-kind prints explore the structure of these genes. Each artwork is unique — if you put them all together, you get the full sequence of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 proteins.
Propensity score weighting
The needs of the many outweigh the needs of the few. —Mr. Spock (Star Trek II)
This month, we explore a related and powerful technique to address bias: propensity score weighting (PSW), which applies weights to each subject instead of matching (or discarding) them.
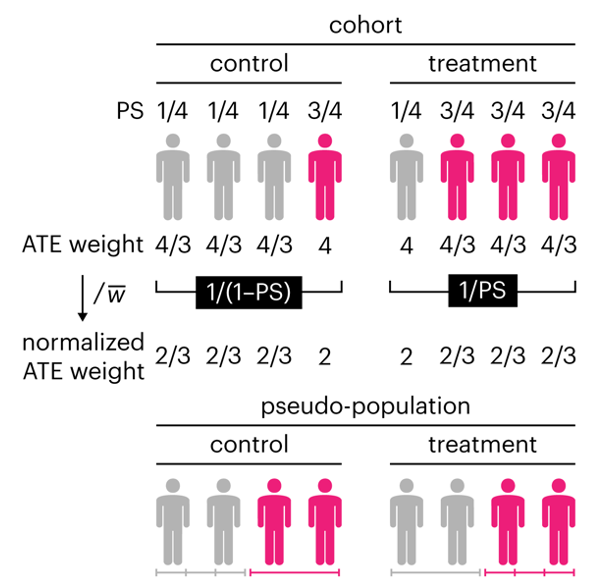
Kurz, C.F., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2025) Points of significance: Propensity score weighting. Nat. Methods 22:1–3.
Happy 2025 π Day—
TTCAGT: a sequence of digits
Celebrate π Day (March 14th) and sequence digits like its 1999. Let's call some peaks.
Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance
I don’t have good luck in the match points. —Rafael Nadal, Spanish tennis player
Points of Significance is an ongoing series of short articles about statistics in Nature Methods that started in 2013. Its aim is to provide clear explanations of essential concepts in statistics for a nonspecialist audience. The articles favor heuristic explanations and make extensive use of simulated examples and graphical explanations, while maintaining mathematical rigor.
Topics range from basic, but often misunderstood, such as uncertainty and P-values, to relatively advanced, but often neglected, such as the error-in-variables problem and the curse of dimensionality. More recent articles have focused on timely topics such as modeling of epidemics, machine learning, and neural networks.
In this article, we discuss the evolution of topics and details behind some of the story arcs, our approach to crafting statistical explanations and narratives, and our use of figures and numerical simulations as props for building understanding.
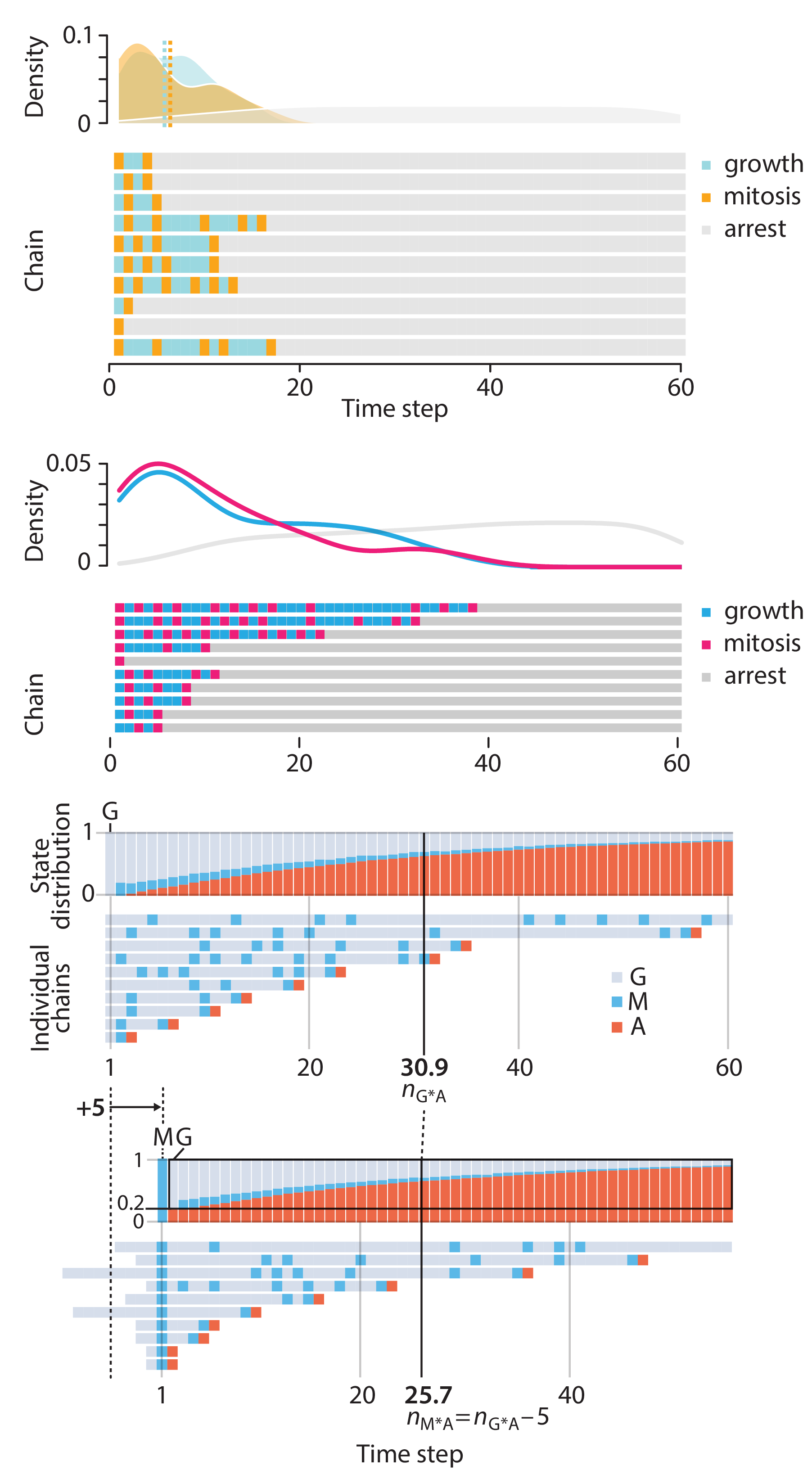
Altman, N. & Krzywinski, M. (2025) Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance. Annual Review of Statistics and Its Application 12:69–87.
Propensity score matching
I don’t have good luck in the match points. —Rafael Nadal, Spanish tennis player
In many experimental designs, we need to keep in mind the possibility of confounding variables, which may give rise to bias in the estimate of the treatment effect.
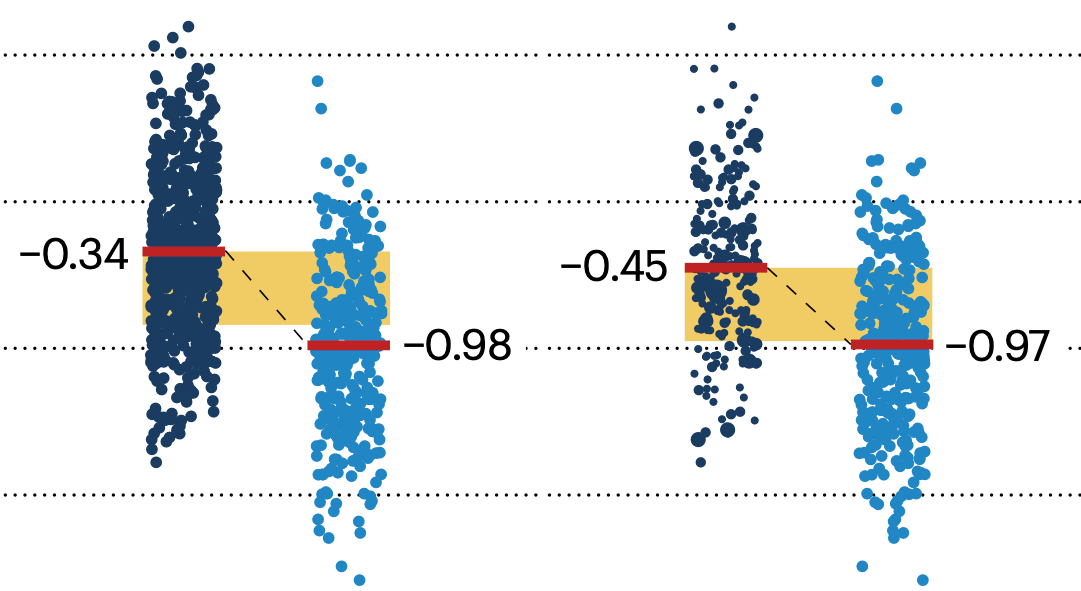
If the control and experimental groups aren't matched (or, roughly, similar enough), this bias can arise.
Sometimes this can be dealt with by randomizing, which on average can balance this effect out. When randomization is not possible, propensity score matching is an excellent strategy to match control and experimental groups.
Kurz, C.F., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2024) Points of significance: Propensity score matching. Nat. Methods 21:1770–1772.
Understanding p-values and significance
P-values combined with estimates of effect size are used to assess the importance of experimental results. However, their interpretation can be invalidated by selection bias when testing multiple hypotheses, fitting multiple models or even informally selecting results that seem interesting after observing the data.
We offer an introduction to principled uses of p-values (targeted at the non-specialist) and identify questionable practices to be avoided.
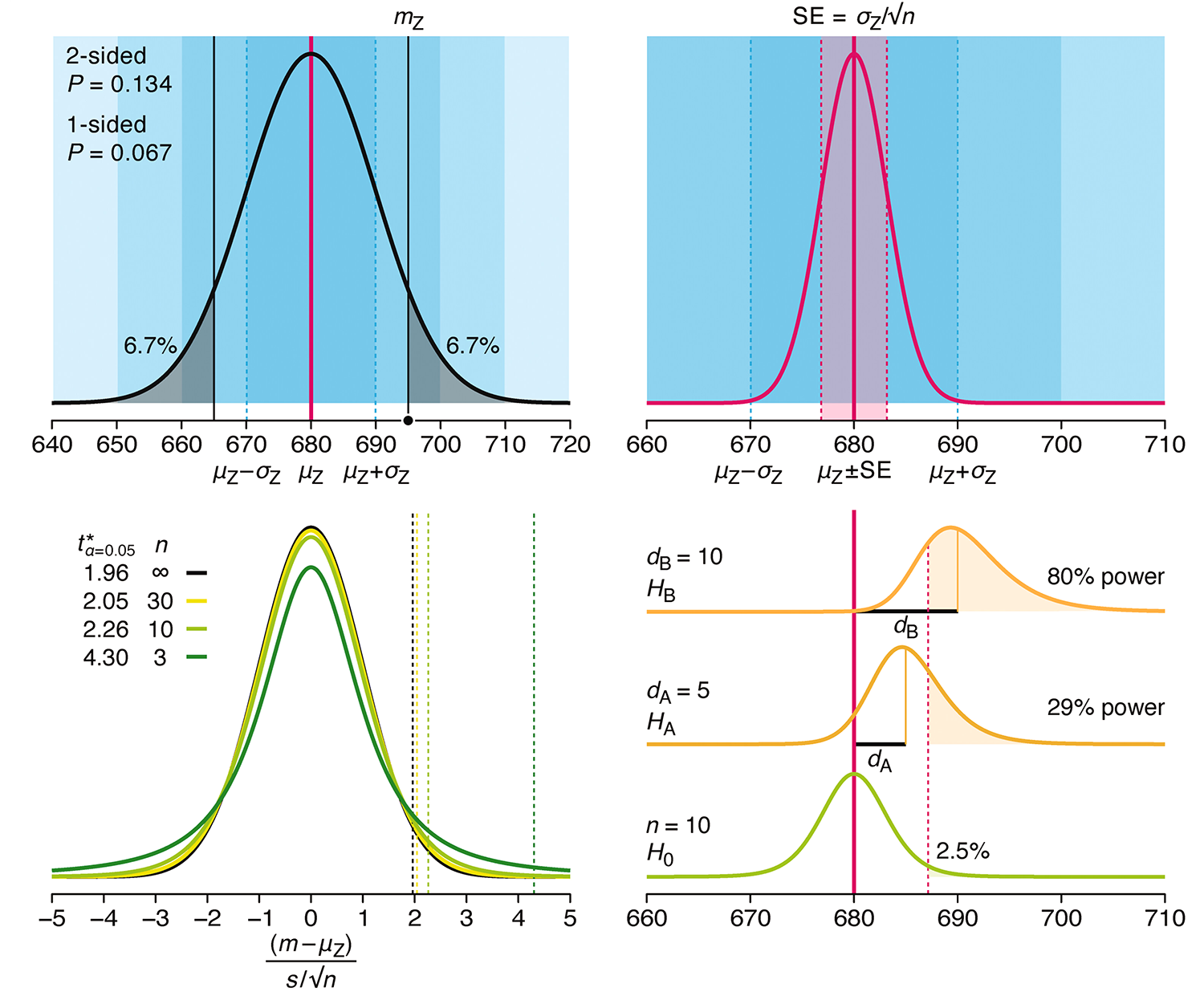
Altman, N. & Krzywinski, M. (2024) Understanding p-values and significance. Laboratory Animals 58:443–446.