Visions of Type
The ampersand originates from the Latin word et, meaning “and” and its form is based on the ligature of ‘e’ and ‘t’. The ampersand used to be the last letter of the English alphabet, which would be recited “... X, Y, Z, and per se and”, with the last phrase slurred to “ampersand”.
Below, sixteen ampersands from different fonts are centered vertically and horizontally. Look how they blend together to reveal a consensus letter.
 buy artwork
buy artwork
To me the ampersand is the letter that I always say yes to.
Beyond Belief Campaign BRCA Art
Fuelled by philanthropy, findings into the workings of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes have led to groundbreaking research and lifesaving innovations to care for families facing cancer.
This set of 100 one-of-a-kind prints explore the structure of these genes. Each artwork is unique — if you put them all together, you get the full sequence of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 proteins.
Propensity score weighting
The needs of the many outweigh the needs of the few. —Mr. Spock (Star Trek II)
This month, we explore a related and powerful technique to address bias: propensity score weighting (PSW), which applies weights to each subject instead of matching (or discarding) them.
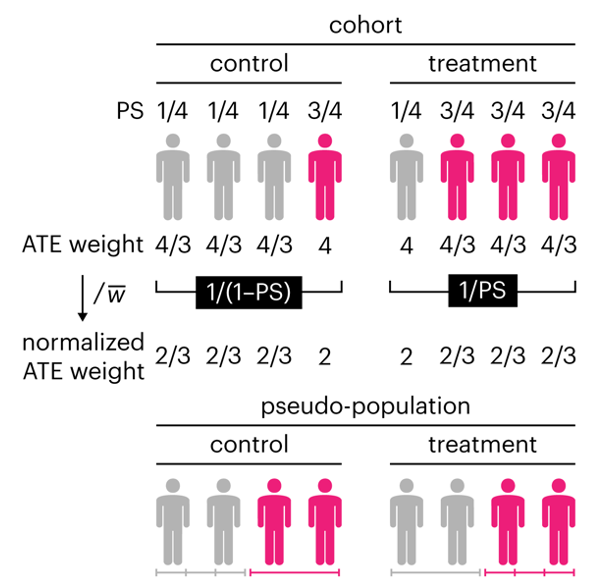
Kurz, C.F., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2025) Points of significance: Propensity score weighting. Nat. Methods 22:1–3.
Happy 2025 π Day—
TTCAGT: a sequence of digits
Celebrate π Day (March 14th) and sequence digits like its 1999. Let's call some peaks.
Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance
I don’t have good luck in the match points. —Rafael Nadal, Spanish tennis player
Points of Significance is an ongoing series of short articles about statistics in Nature Methods that started in 2013. Its aim is to provide clear explanations of essential concepts in statistics for a nonspecialist audience. The articles favor heuristic explanations and make extensive use of simulated examples and graphical explanations, while maintaining mathematical rigor.
Topics range from basic, but often misunderstood, such as uncertainty and P-values, to relatively advanced, but often neglected, such as the error-in-variables problem and the curse of dimensionality. More recent articles have focused on timely topics such as modeling of epidemics, machine learning, and neural networks.
In this article, we discuss the evolution of topics and details behind some of the story arcs, our approach to crafting statistical explanations and narratives, and our use of figures and numerical simulations as props for building understanding.
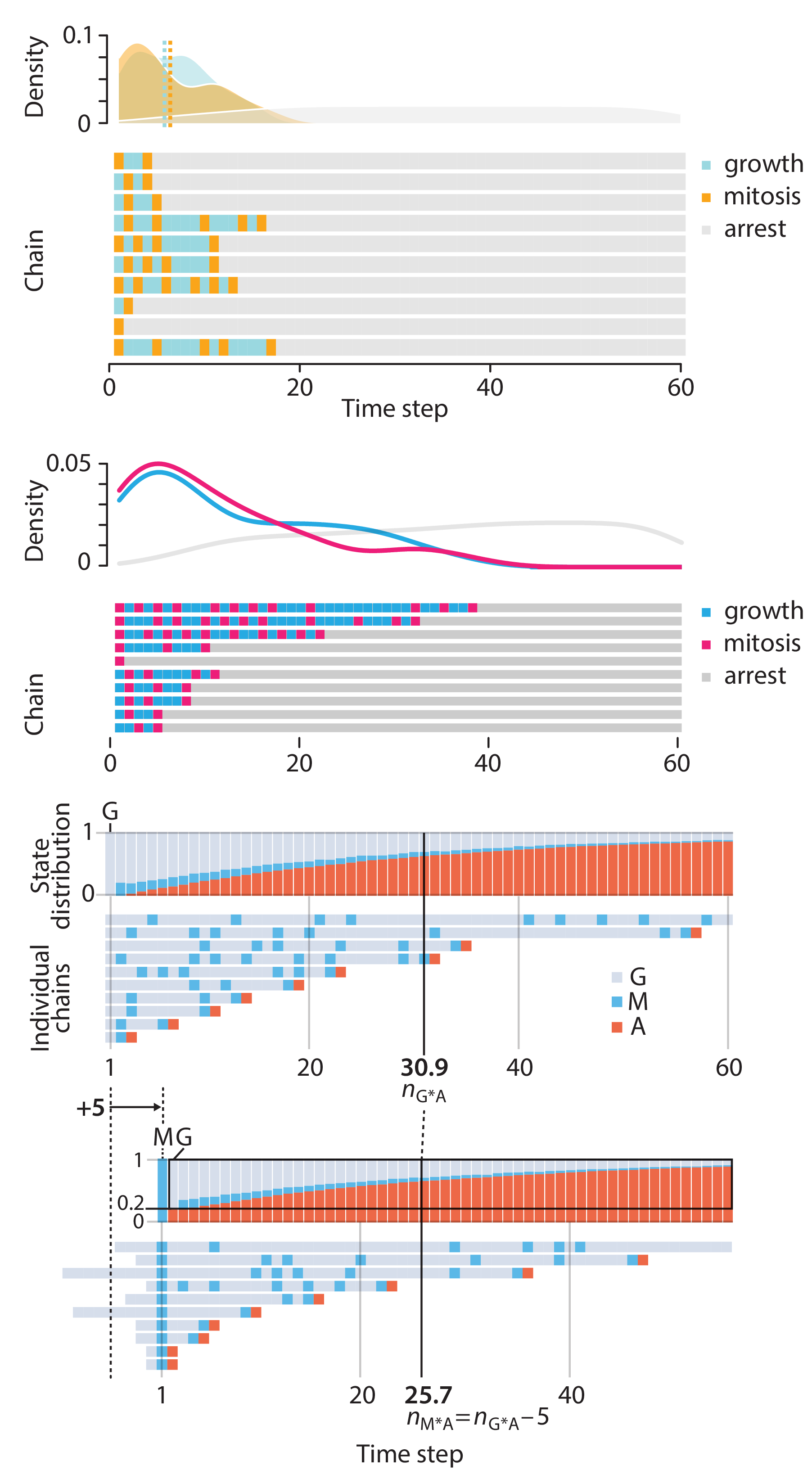
Altman, N. & Krzywinski, M. (2025) Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance. Annual Review of Statistics and Its Application 12:69–87.
Propensity score matching
I don’t have good luck in the match points. —Rafael Nadal, Spanish tennis player
In many experimental designs, we need to keep in mind the possibility of confounding variables, which may give rise to bias in the estimate of the treatment effect.
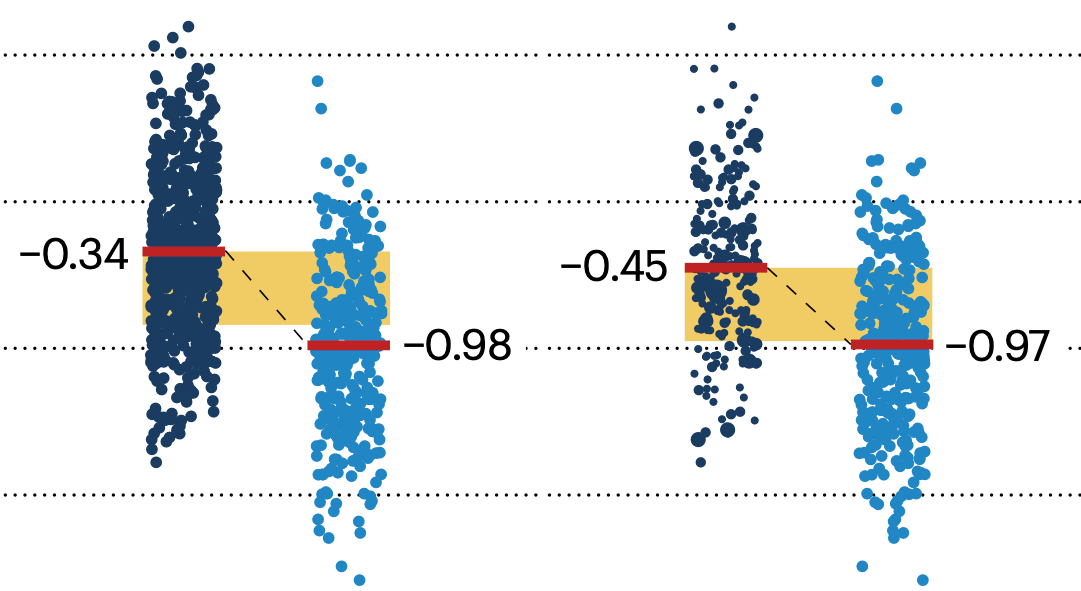
If the control and experimental groups aren't matched (or, roughly, similar enough), this bias can arise.
Sometimes this can be dealt with by randomizing, which on average can balance this effect out. When randomization is not possible, propensity score matching is an excellent strategy to match control and experimental groups.
Kurz, C.F., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2024) Points of significance: Propensity score matching. Nat. Methods 21:1770–1772.