Nature Methods: Points of Significance

Martin Krzywinski is a staff scientist at Canada’s Michael Smith Genome Sciences Centre.
Naomi Altman is a Professor of Statistics at The Pennsylvania State University.
contributing authors
Paul Blainey is an Assistant Professor of Biological Engineering at MIT and Core Member of the Broad Institute.
Danilo Bzdok is an Assistant Professor at the Department of Psychiatry, RWTH Aachen University, Germany, and a Visiting Professor at INRIA/Neurospin Saclay in France.
Kiranmoy Das is a faculty member at the Indian Statistical Institute in Kolkata, India.
Luca Greco is an Assistant Professor of Statistics at the University of Sannio in Benevento, Italy.
Jasleen Grewal is a graduate student in the Jones lab at Canada's Michael Smith Genome Sciences Centre.
Anthony Kulesa is a graduate student in the Department of Biological Engineering at MIT.
Christoph Kurz is a researcher at Novartis Pharma GmbH, Munich, Germany.
Jake Lever is a Postdoctoral Research Fellow in Bioengineering at Stanford University in Stanford, California, USA.
Geroge Luta Associate Professor of Biostatistics at the Georgetown University in Washington, DC, USA.
Jorge López Puga is a Professor of Research Methodology at UCAM Universidad Católica de Murcia.
Byran Smucker is an Associate Professor of Statistics at Miami University in Oxford, OH, USA.
Bernhard Voelkl is a Postdoctoral Research Fellow in the Division of Animal Welfare at the Veterinary Public Health Institute, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
Hanno Würbel is a Professor in the Division of Animal Welfare at the Veterinary Public Health Institute, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
Propensity score weighting
The needs of the many outweigh the needs of the few. —Mr. Spock (Star Trek II)
This month, we explore a related and powerful technique to address bias: propensity score weighting (PSW), which applies weights to each subject instead of matching (or discarding) them.
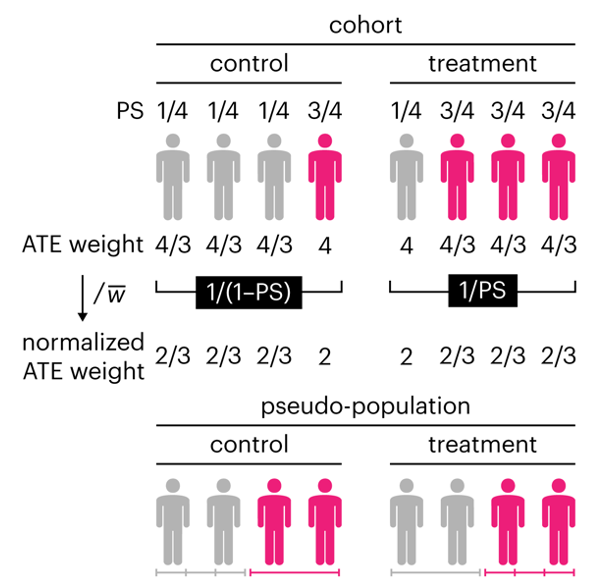
Kurz, C.F., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2025) Points of significance: Propensity score weighting. Nat. Methods 22:1–3.
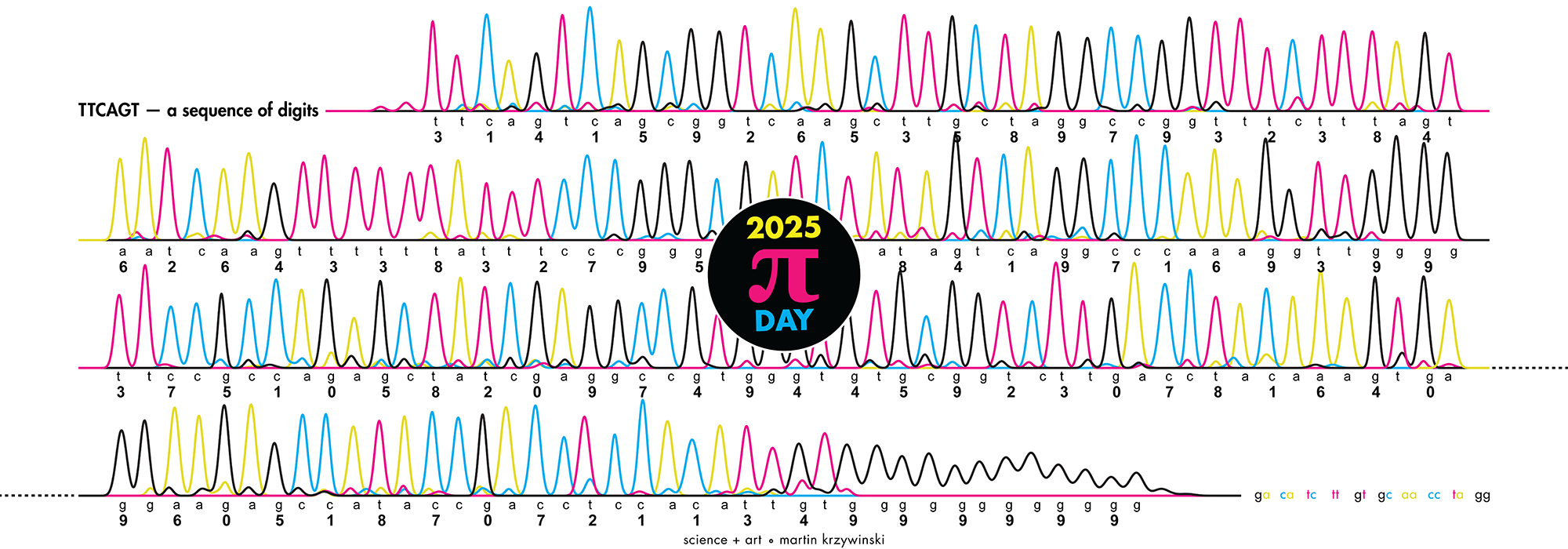
Happy 2025 π Day—
TTCAGT: a sequence of digits
Celebrate π Day (March 14th) and sequence digits like its 1999. Let's call some peaks.
Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance
I don’t have good luck in the match points. —Rafael Nadal, Spanish tennis player
Points of Significance is an ongoing series of short articles about statistics in Nature Methods that started in 2013. Its aim is to provide clear explanations of essential concepts in statistics for a nonspecialist audience. The articles favor heuristic explanations and make extensive use of simulated examples and graphical explanations, while maintaining mathematical rigor.
Topics range from basic, but often misunderstood, such as uncertainty and P-values, to relatively advanced, but often neglected, such as the error-in-variables problem and the curse of dimensionality. More recent articles have focused on timely topics such as modeling of epidemics, machine learning, and neural networks.
In this article, we discuss the evolution of topics and details behind some of the story arcs, our approach to crafting statistical explanations and narratives, and our use of figures and numerical simulations as props for building understanding.
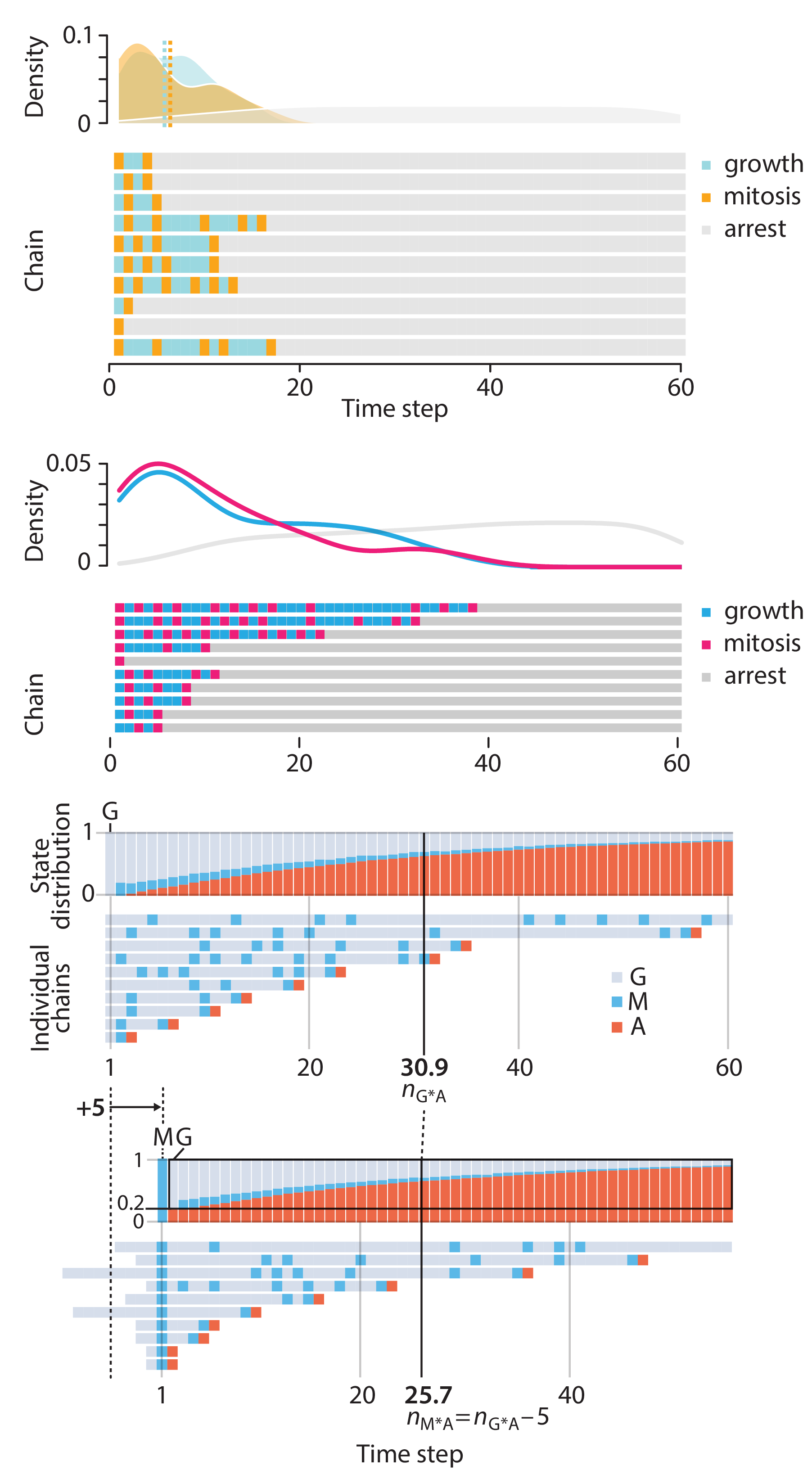
Altman, N. & Krzywinski, M. (2025) Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance. Annual Review of Statistics and Its Application 12:69–87.
Propensity score matching
I don’t have good luck in the match points. —Rafael Nadal, Spanish tennis player
In many experimental designs, we need to keep in mind the possibility of confounding variables, which may give rise to bias in the estimate of the treatment effect.
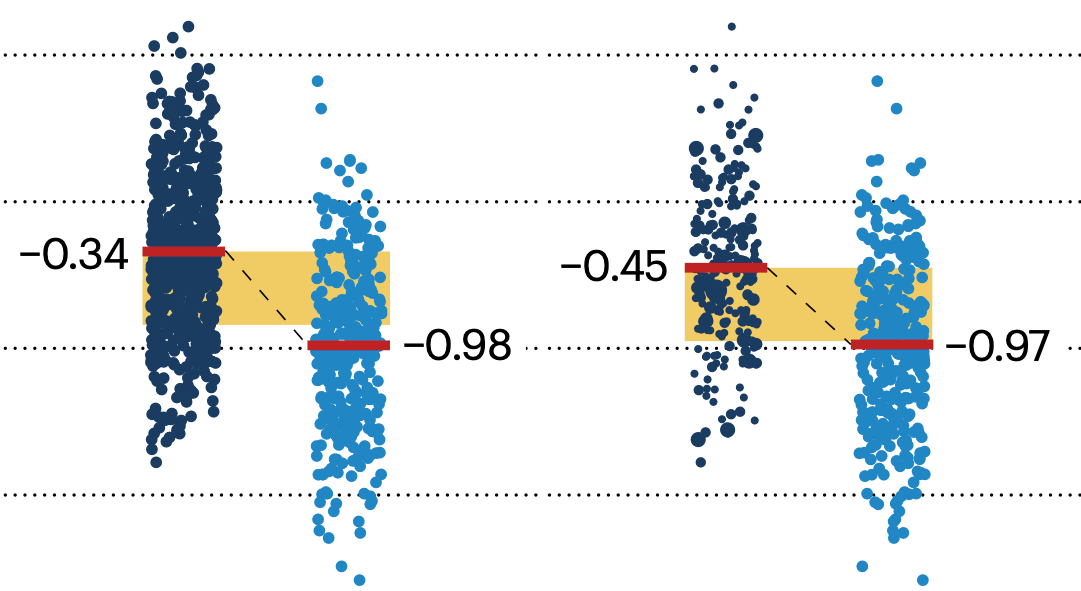
If the control and experimental groups aren't matched (or, roughly, similar enough), this bias can arise.
Sometimes this can be dealt with by randomizing, which on average can balance this effect out. When randomization is not possible, propensity score matching is an excellent strategy to match control and experimental groups.
Kurz, C.F., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2024) Points of significance: Propensity score matching. Nat. Methods 21:1770–1772.