Nature Methods: Points of Significance

Access all columns for free at Statistics for Biologists Nature Collection.
A Statistics Primer and Best Practices
The Points of Significance column was launched in September 2013 as an educational resource to authors and to provide practical suggestions about best practices in statistical analysis and reporting.
This month we launch a new column "Points of Significance" devoted to statistics, a topic of profound importance for biological research, but one that often doesn’t receive the attention it deserves.
The "aura of exactitude" that often surrounds statistics is one of the main notions that the Points of Significance column will attempt to dispel, while providing useful pointers on using and evaluating statistical measures.
—Dan Evanko, Let's Give Statistics the Attention it Deserves in Biological Research
The column is co-authored with Naomi Altman (Pennsylvania State University). Paul Blainey (Broad) is a contributing co-author.
Free Access
In February 2015, Nature Methods announced that the entire Points of Significance collection will be free.
When Nature Methods launched the Points of Significance column over a year ago we were hopeful that those biologists with a limited background in statistics, or who just needed a refresher, would find it accessible and useful for helping them improve the statistical rigor of their research. We have since received comments from researchers and educators in fields ranging from biology to meteorology who say they read the column regularly and use it in their courses. Hearing that the column has had a wider impact than we anticipated has been very encouraging and we hope the column continues for quite some time.
—Dan Evanko, Points of Significance now free access
Also, in a recent post on the ofschemesandmemes blog, a new statistics collection for biologists was announced.
The pieces range from comments, to advice on very specific experimental approaches, to the entire collection of the Points of Significance columns that address basic concepts in statistics in an experimental biology context. These columns, originally published in Nature Methods thanks to Martin Krzywinski and guest editor Naomi Altman, have already proven very popular with readers and teachers. Finally, the collection presents a web tool to create box plots among other resources.
—Veronique Kiermer, Statistics for biologists—A free Nature Collection
continuity and consistency
Each column is written with continuity and consistency in mind. Our goal is to never rely on concepts that we have not previously discussed. We do not assume previous statistical knowledge—only basic math. Concepts are illustrated using practical examples that embody the ideas without extraneous complicated details. All of the figures are designed with the same approach—as simple and self-contained as possible.
Beyond Belief Campaign BRCA Art
Fuelled by philanthropy, findings into the workings of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes have led to groundbreaking research and lifesaving innovations to care for families facing cancer.
This set of 100 one-of-a-kind prints explore the structure of these genes. Each artwork is unique — if you put them all together, you get the full sequence of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 proteins.
Propensity score weighting
The needs of the many outweigh the needs of the few. —Mr. Spock (Star Trek II)
This month, we explore a related and powerful technique to address bias: propensity score weighting (PSW), which applies weights to each subject instead of matching (or discarding) them.
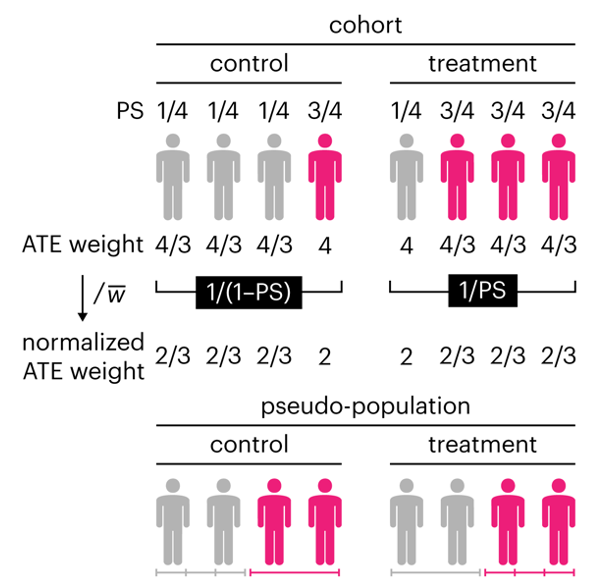
Kurz, C.F., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2025) Points of significance: Propensity score weighting. Nat. Methods 22:1–3.
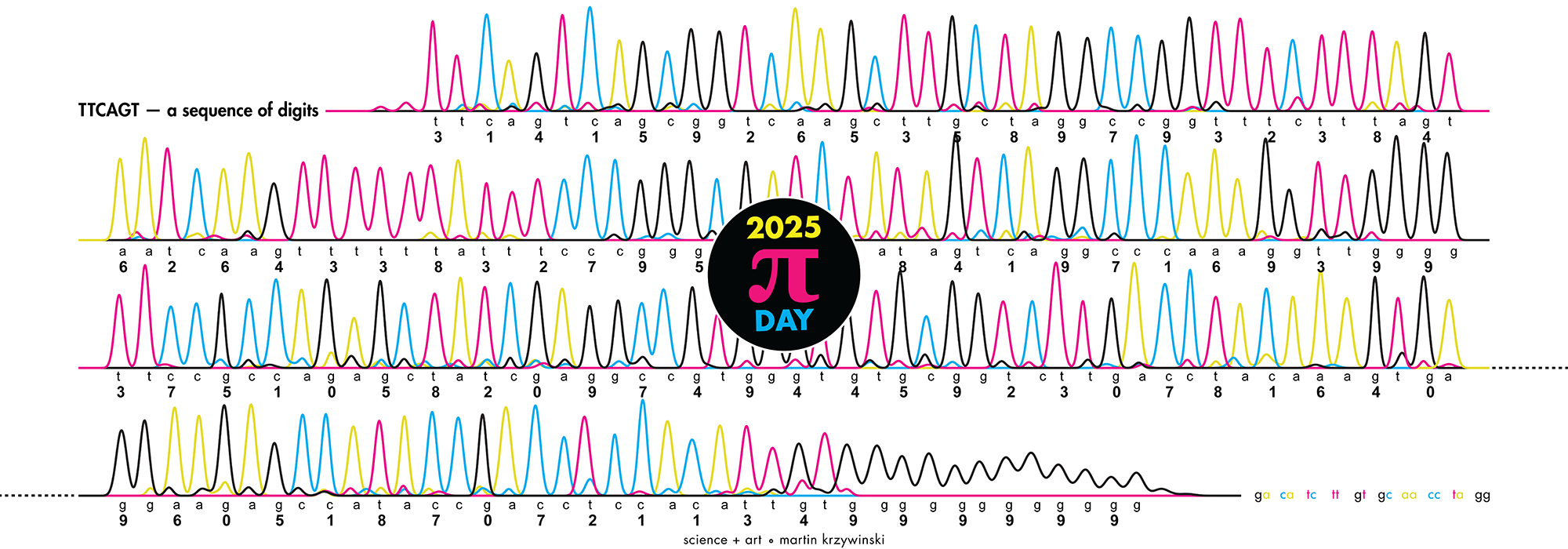
Happy 2025 π Day—
TTCAGT: a sequence of digits
Celebrate π Day (March 14th) and sequence digits like its 1999. Let's call some peaks.
Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance
I don’t have good luck in the match points. —Rafael Nadal, Spanish tennis player
Points of Significance is an ongoing series of short articles about statistics in Nature Methods that started in 2013. Its aim is to provide clear explanations of essential concepts in statistics for a nonspecialist audience. The articles favor heuristic explanations and make extensive use of simulated examples and graphical explanations, while maintaining mathematical rigor.
Topics range from basic, but often misunderstood, such as uncertainty and P-values, to relatively advanced, but often neglected, such as the error-in-variables problem and the curse of dimensionality. More recent articles have focused on timely topics such as modeling of epidemics, machine learning, and neural networks.
In this article, we discuss the evolution of topics and details behind some of the story arcs, our approach to crafting statistical explanations and narratives, and our use of figures and numerical simulations as props for building understanding.
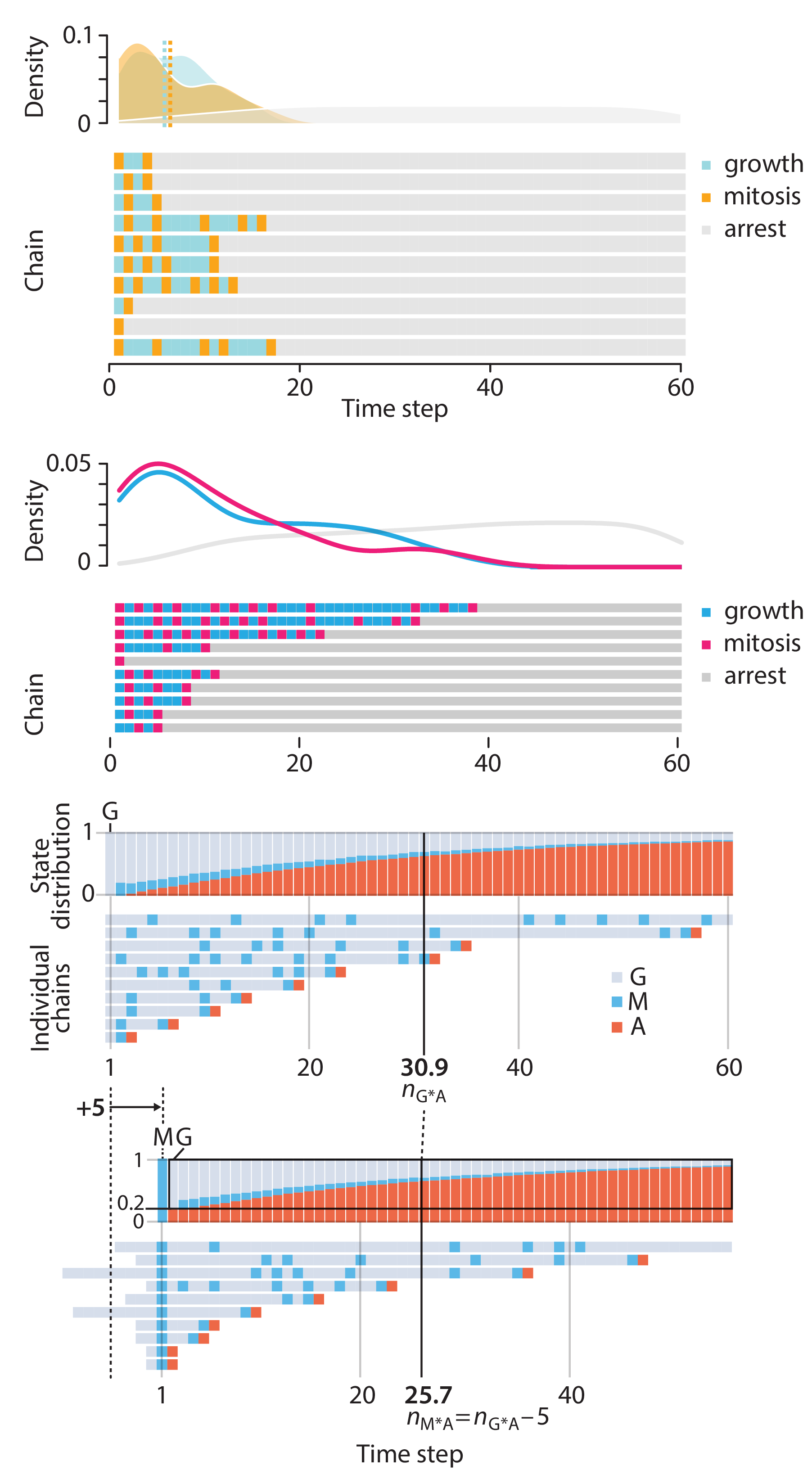
Altman, N. & Krzywinski, M. (2025) Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance. Annual Review of Statistics and Its Application 12:69–87.