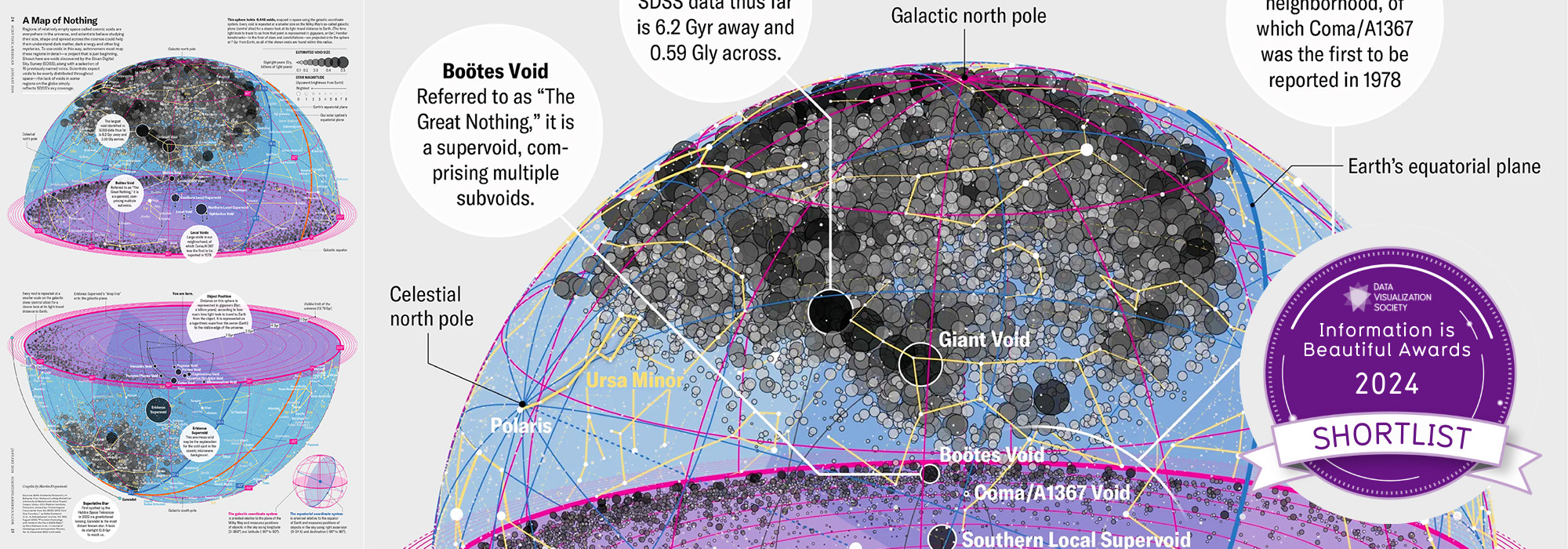
Nature Methods: Points of View
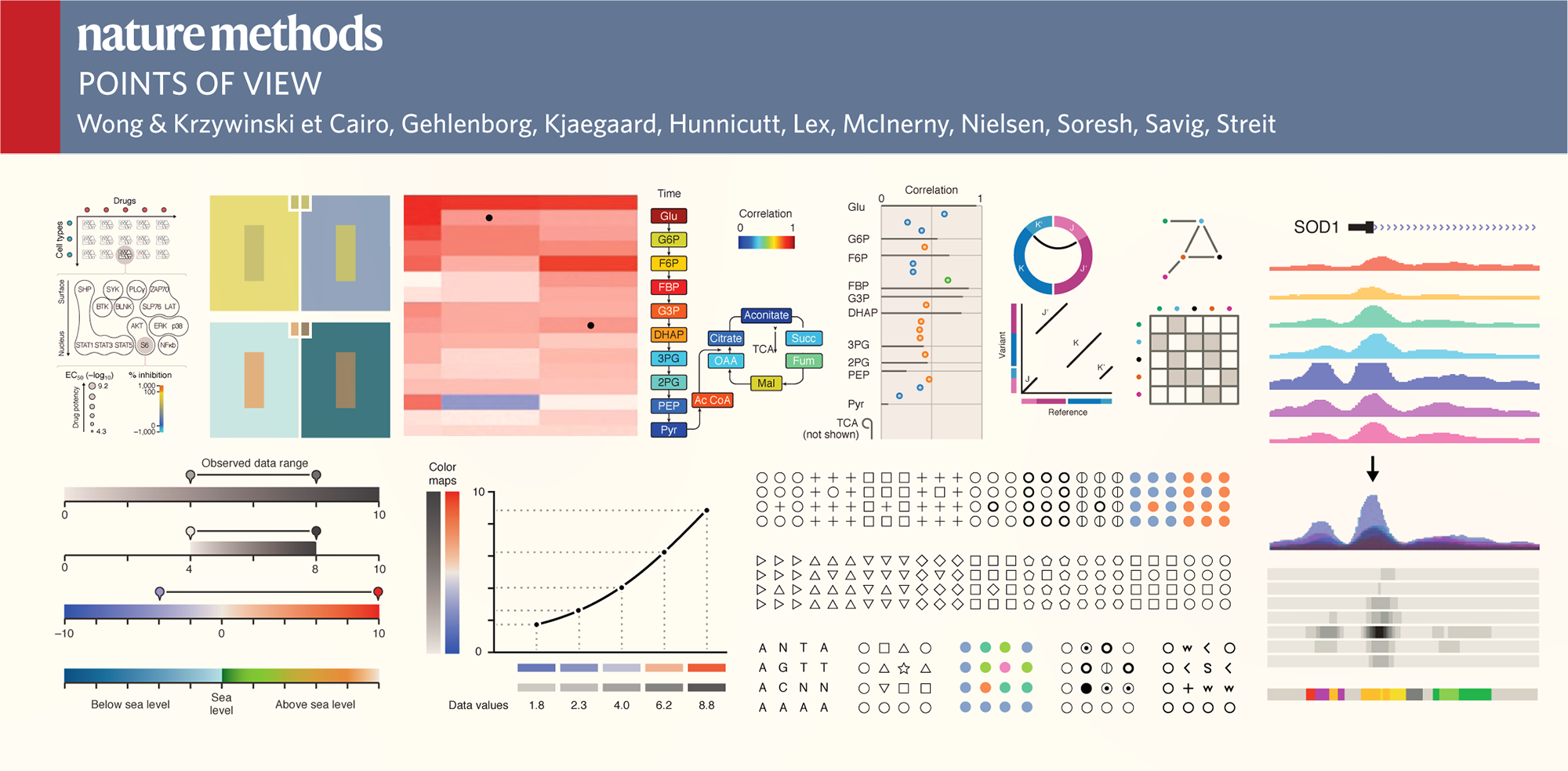
Bang Wong is the creative director of the Broad Institute and an adjunct assistant professor in the Department of Art as Applied to Medicine at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
Nils Gehlenborg is a research associate at Harvard Medical School.
Martin Krzywinski is a staff scientist at Canada’s Michael Smith Genome Sciences Centre.
Marc Streit is an assistant professor of computer science at Johannes Kepler University Linz.
Cydney Nielsen is a Research Associate at the BC Cancer Research Center.
Rikke Schmidt Kjærgaard is an assistant professor in the Interdisciplinary Nanoscience Center at Aarhus University.
Noam Shoresh is a senior computational biologist at the Broad Institute
Erica Savig is a PhD candidate in Cancer Biology at Stanford University.
Alberto Cairo is a Professor of Professional Practice at the School of Communication of the University of Miami.
Alexander Lex is a postdoctoral fellow in computer science at Harvard University.
Gregor McInerny is a Senior Research Fellow at the Department of Computer Science, University of Oxford.
Barbara J. Hunnicutt is a research assistant at Oregon Health and Science University.
Beyond Belief Campaign BRCA Art
Fuelled by philanthropy, findings into the workings of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes have led to groundbreaking research and lifesaving innovations to care for families facing cancer.
This set of 100 one-of-a-kind prints explore the structure of these genes. Each artwork is unique — if you put them all together, you get the full sequence of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 proteins.
Propensity score weighting
The needs of the many outweigh the needs of the few. —Mr. Spock (Star Trek II)
This month, we explore a related and powerful technique to address bias: propensity score weighting (PSW), which applies weights to each subject instead of matching (or discarding) them.
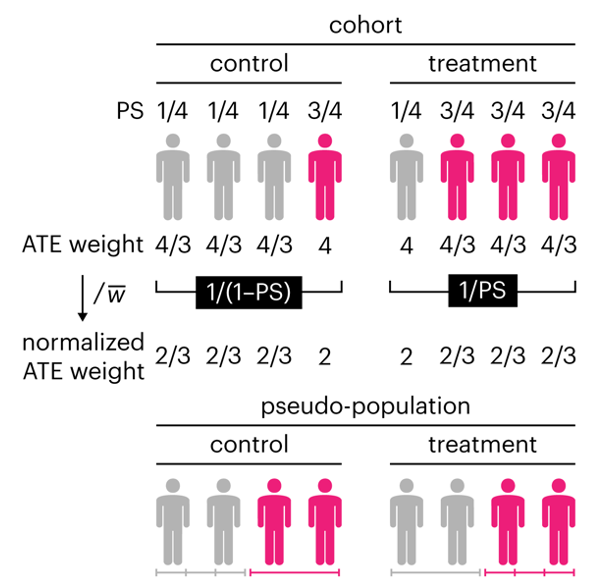
Kurz, C.F., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2025) Points of significance: Propensity score weighting. Nat. Methods 22:1–3.
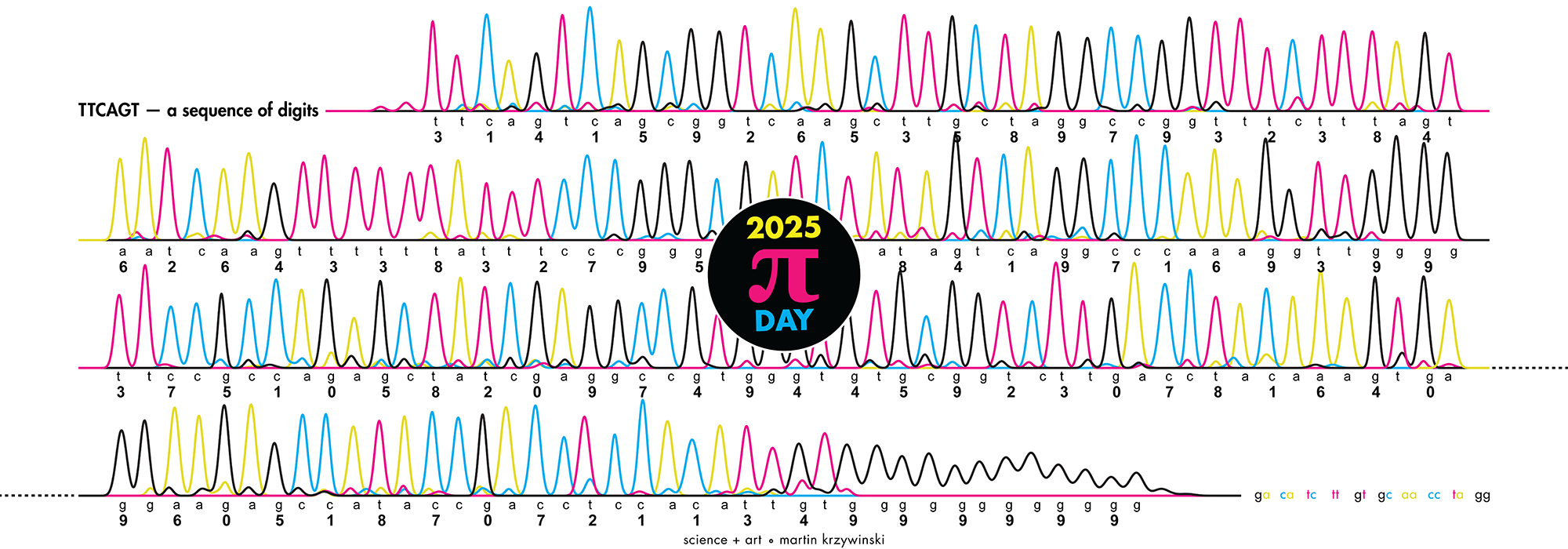
Happy 2025 π Day—
TTCAGT: a sequence of digits
Celebrate π Day (March 14th) and sequence digits like its 1999. Let's call some peaks.
Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance
I don’t have good luck in the match points. —Rafael Nadal, Spanish tennis player
Points of Significance is an ongoing series of short articles about statistics in Nature Methods that started in 2013. Its aim is to provide clear explanations of essential concepts in statistics for a nonspecialist audience. The articles favor heuristic explanations and make extensive use of simulated examples and graphical explanations, while maintaining mathematical rigor.
Topics range from basic, but often misunderstood, such as uncertainty and P-values, to relatively advanced, but often neglected, such as the error-in-variables problem and the curse of dimensionality. More recent articles have focused on timely topics such as modeling of epidemics, machine learning, and neural networks.
In this article, we discuss the evolution of topics and details behind some of the story arcs, our approach to crafting statistical explanations and narratives, and our use of figures and numerical simulations as props for building understanding.
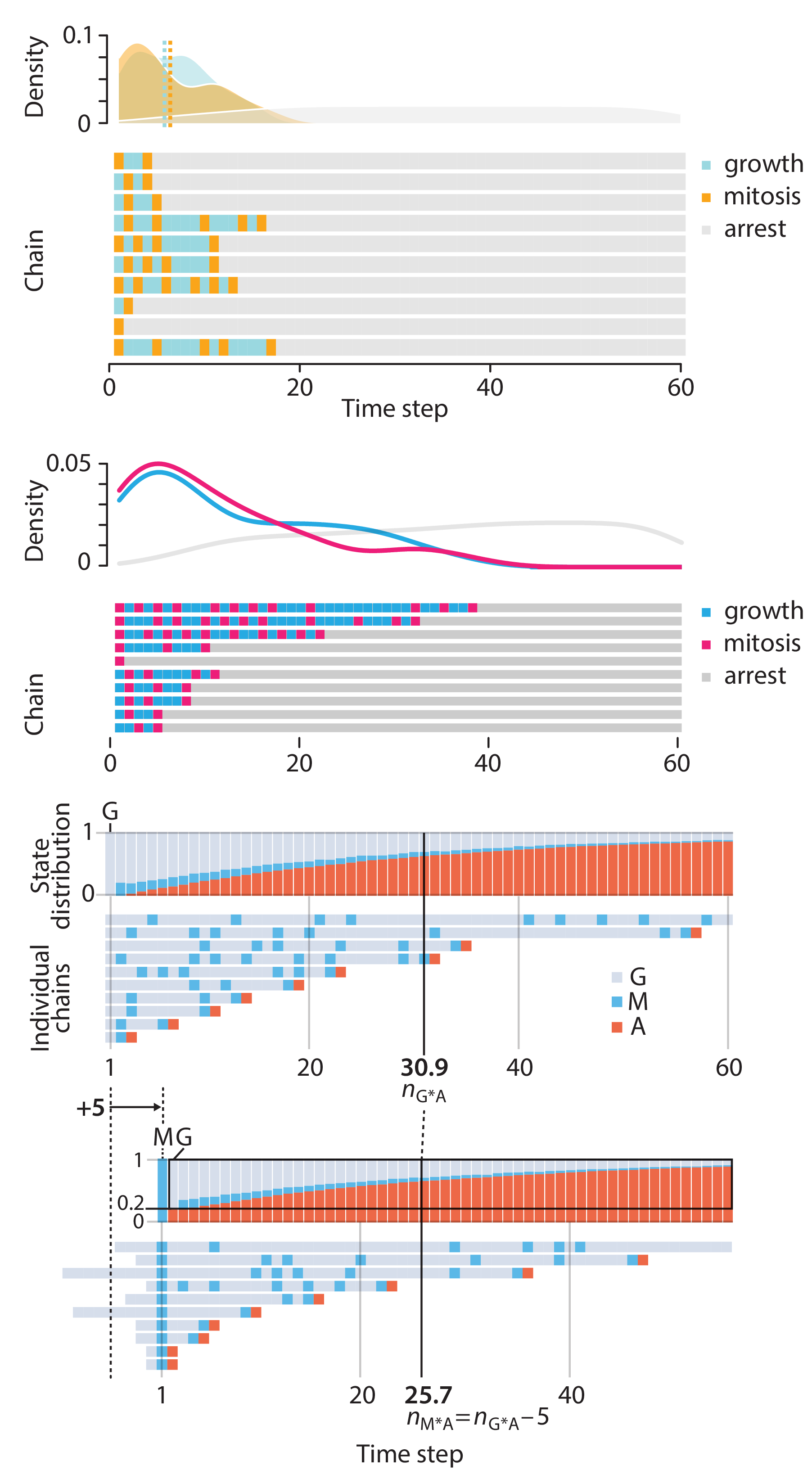
Altman, N. & Krzywinski, M. (2025) Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance. Annual Review of Statistics and Its Application 12:69–87.