Art of the Personalized Oncogenomics Program
Nature uses only the longest threads to weave her patterns, so that each small piece of her fabric reveals the organization of the entire tapestry.
— Richard Feynman
I've prepared posters in three popular size formats: 11" × 14", 50 cm × 50 cm and 50 cm × 70 cm.
All artwork is available in PDF and PNG format. Click on the button on the top-right of the image to download these files. All files include 1/8" bleed. For printing, use the PDFs.
The PNG bitmap is provided for convenience and rastered at 600 dpi with 1/8" bleed (75 pixel margin on all sides). For example, the 11" × 14" bitmap has width 11.25 × 600 = 6,750 and height 14.25 × 600 = 8,550.
An explanation of how these images were generated, along with a printable legend, is available in the Methods section.
These posters are designed to fit a standard 11" × 14" frame.

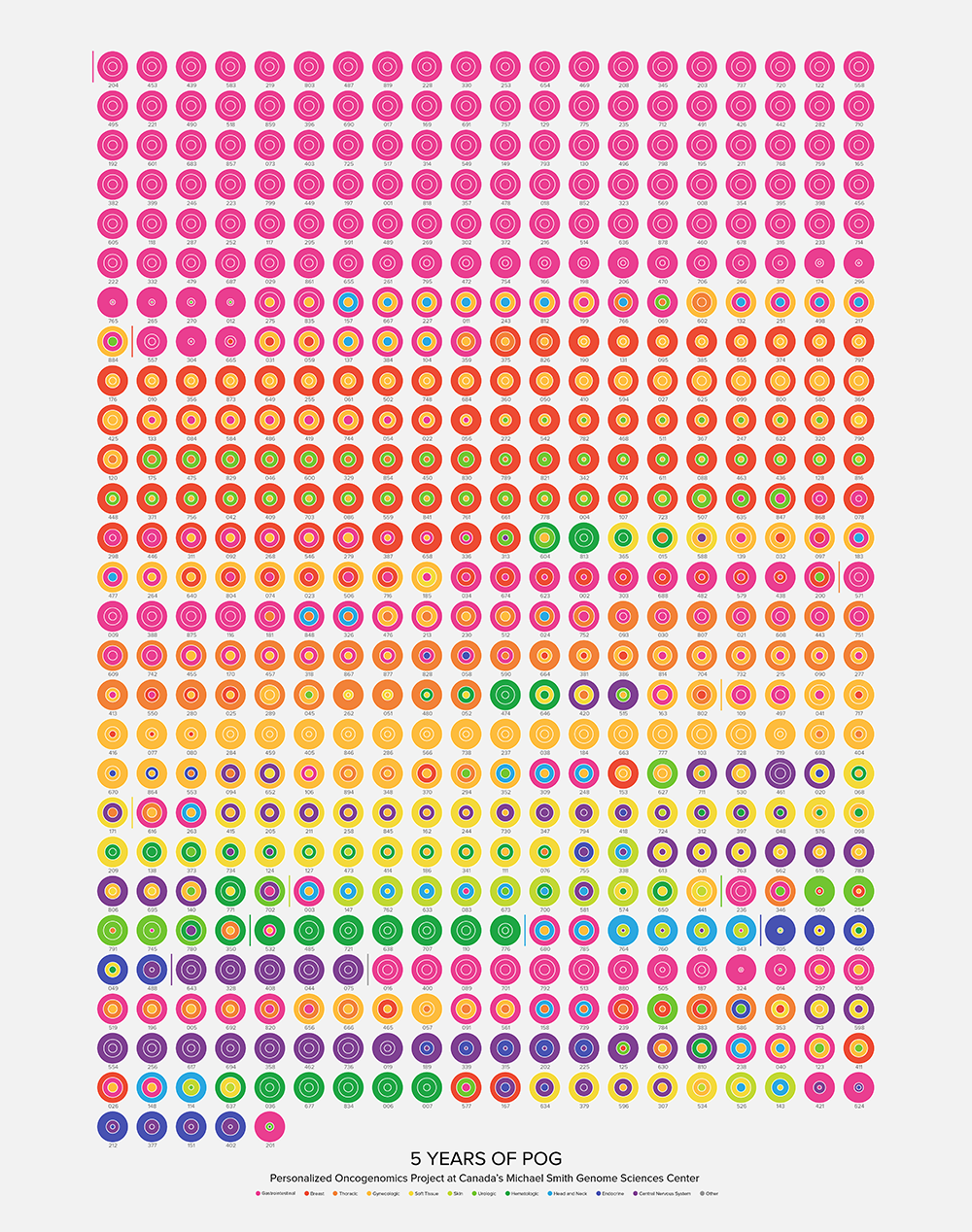
These posters are fit to 50 cm × 70 cm and fit into inexpensive Strömby frames at IKEA.
The bigmap is 600 dpi (artboard 11,811 × 16,535 pixels) with 1/8" bleed (75 pixel margin on all sides).

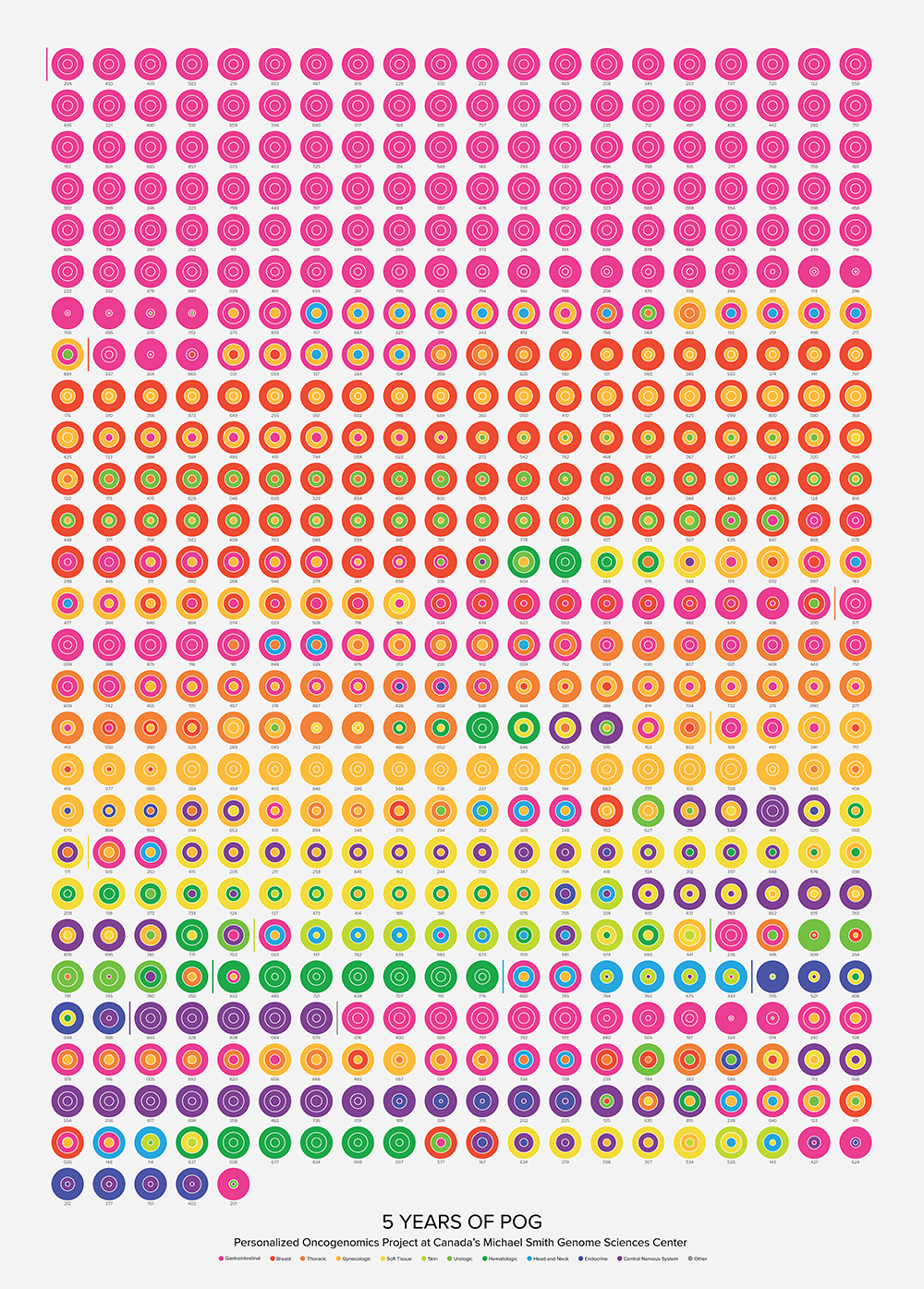
These posters are fit to 50 cm × 50 cm and fit into inexpensive Strömby frames at IKEA.
You can print this poster to any square frame but keep in mind that if you shrink it down too much, the text may not be legible. At size, the text is 6.7 pt, which can be read comfortably. I would avoid printing the poster smaller than 30 cm × 30cm, which would have text of 4 pt in size.
The bigmap is 600 dpi (artboard 11,811 × 16,535 pixels) with 1/8" bleed (75 pixel margin on all sides).

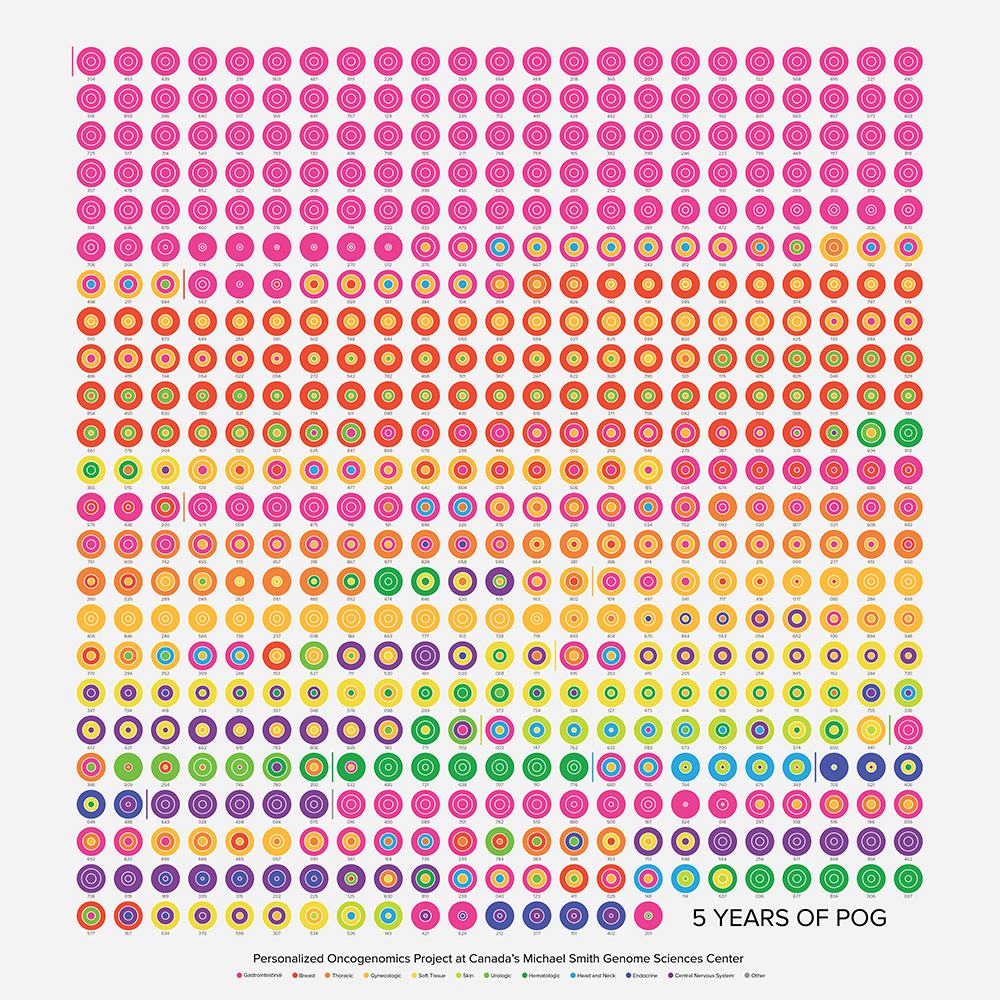
This is the standard postcard size. The bitmap is 600 dpi (artboard 2,400 × 3,600 pixels) with 1/8" bleed (75 pixel margin on all sides).

Beyond Belief Campaign BRCA Art
Fuelled by philanthropy, findings into the workings of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes have led to groundbreaking research and lifesaving innovations to care for families facing cancer.
This set of 100 one-of-a-kind prints explore the structure of these genes. Each artwork is unique — if you put them all together, you get the full sequence of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 proteins.
Propensity score weighting
The needs of the many outweigh the needs of the few. —Mr. Spock (Star Trek II)
This month, we explore a related and powerful technique to address bias: propensity score weighting (PSW), which applies weights to each subject instead of matching (or discarding) them.
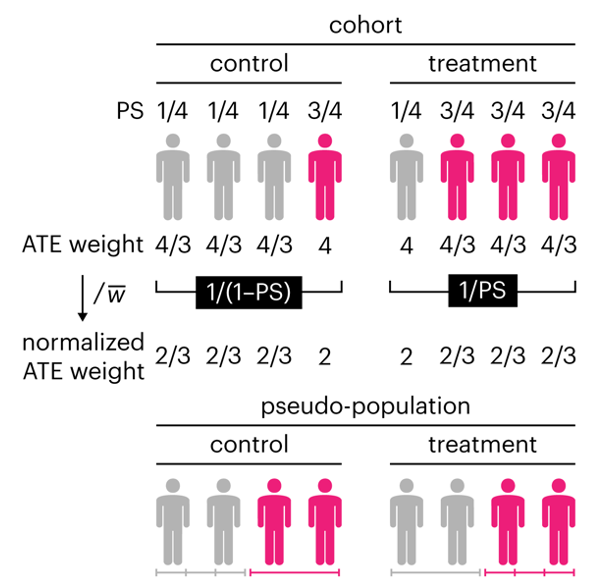
Kurz, C.F., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2025) Points of significance: Propensity score weighting. Nat. Methods 22:1–3.
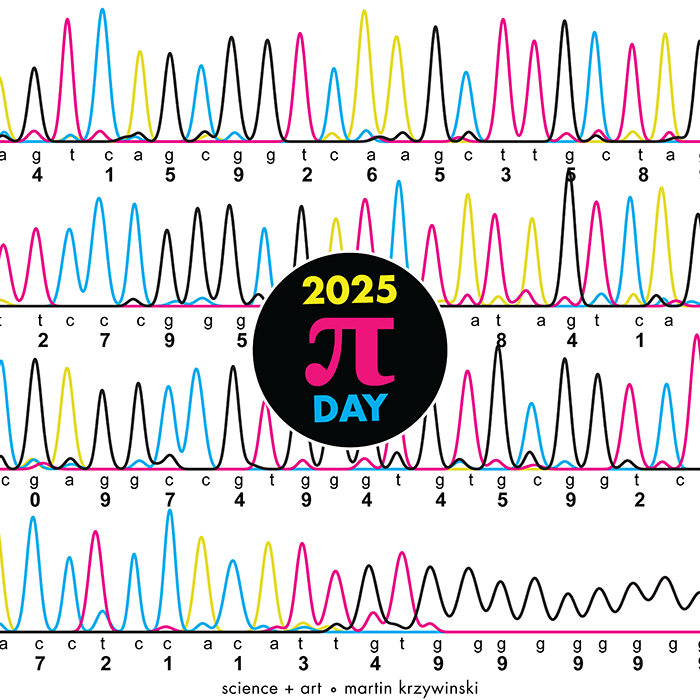
Happy 2025 π Day—
TTCAGT: a sequence of digits
Celebrate π Day (March 14th) and sequence digits like its 1999. Let's call some peaks.
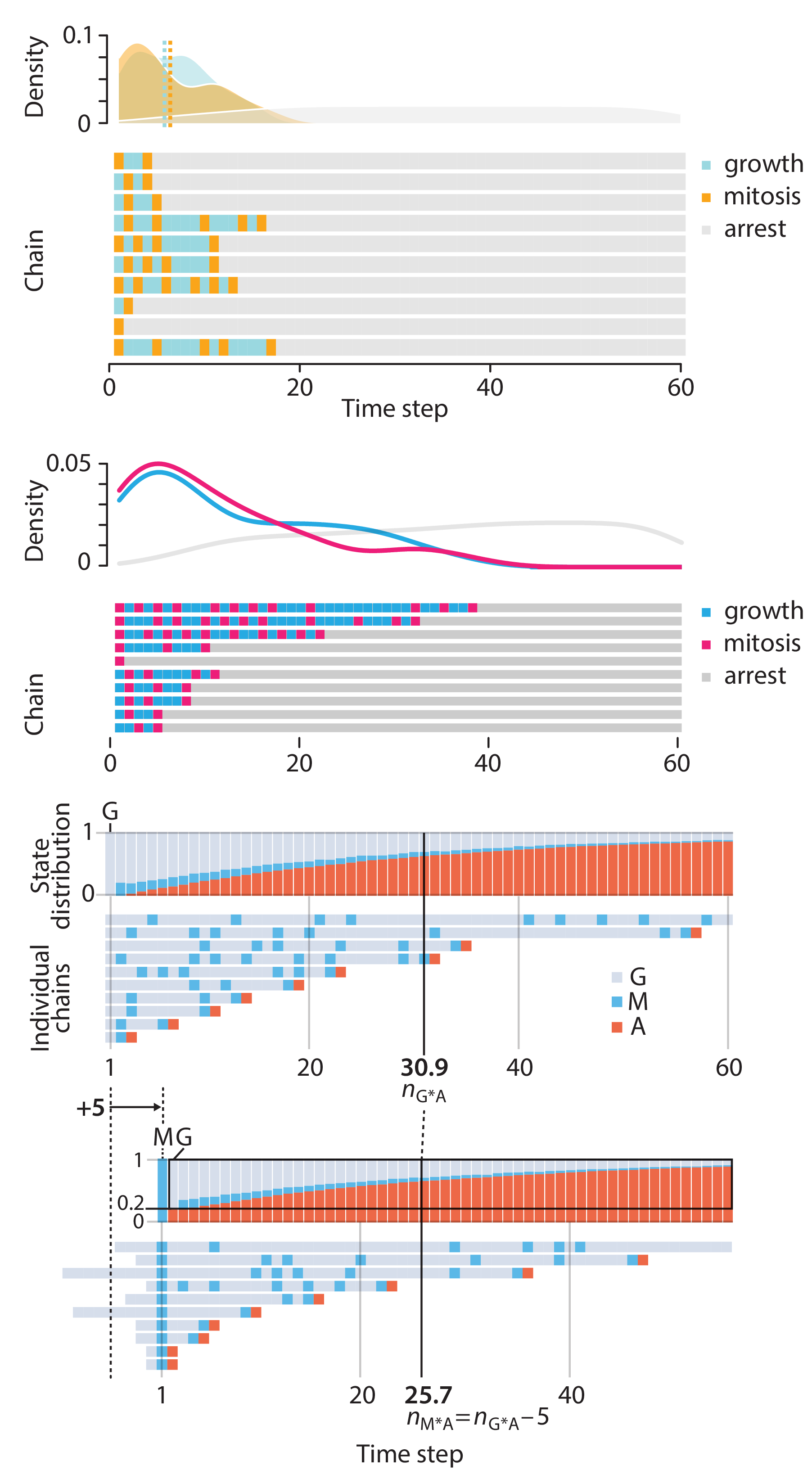
Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance
I don’t have good luck in the match points. —Rafael Nadal, Spanish tennis player
Points of Significance is an ongoing series of short articles about statistics in Nature Methods that started in 2013. Its aim is to provide clear explanations of essential concepts in statistics for a nonspecialist audience. The articles favor heuristic explanations and make extensive use of simulated examples and graphical explanations, while maintaining mathematical rigor.
Topics range from basic, but often misunderstood, such as uncertainty and P-values, to relatively advanced, but often neglected, such as the error-in-variables problem and the curse of dimensionality. More recent articles have focused on timely topics such as modeling of epidemics, machine learning, and neural networks.
In this article, we discuss the evolution of topics and details behind some of the story arcs, our approach to crafting statistical explanations and narratives, and our use of figures and numerical simulations as props for building understanding.
Altman, N. & Krzywinski, M. (2025) Crafting 10 Years of Statistics Explanations: Points of Significance. Annual Review of Statistics and Its Application 12:69–87.
Propensity score matching
I don’t have good luck in the match points. —Rafael Nadal, Spanish tennis player
In many experimental designs, we need to keep in mind the possibility of confounding variables, which may give rise to bias in the estimate of the treatment effect.
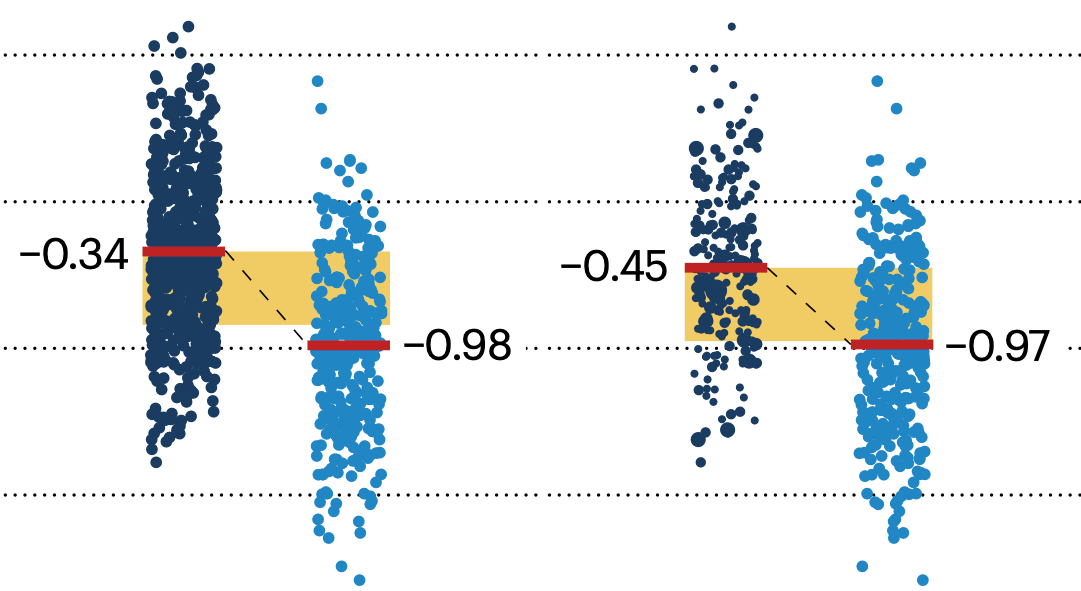
If the control and experimental groups aren't matched (or, roughly, similar enough), this bias can arise.
Sometimes this can be dealt with by randomizing, which on average can balance this effect out. When randomization is not possible, propensity score matching is an excellent strategy to match control and experimental groups.
Kurz, C.F., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N. (2024) Points of significance: Propensity score matching. Nat. Methods 21:1770–1772.
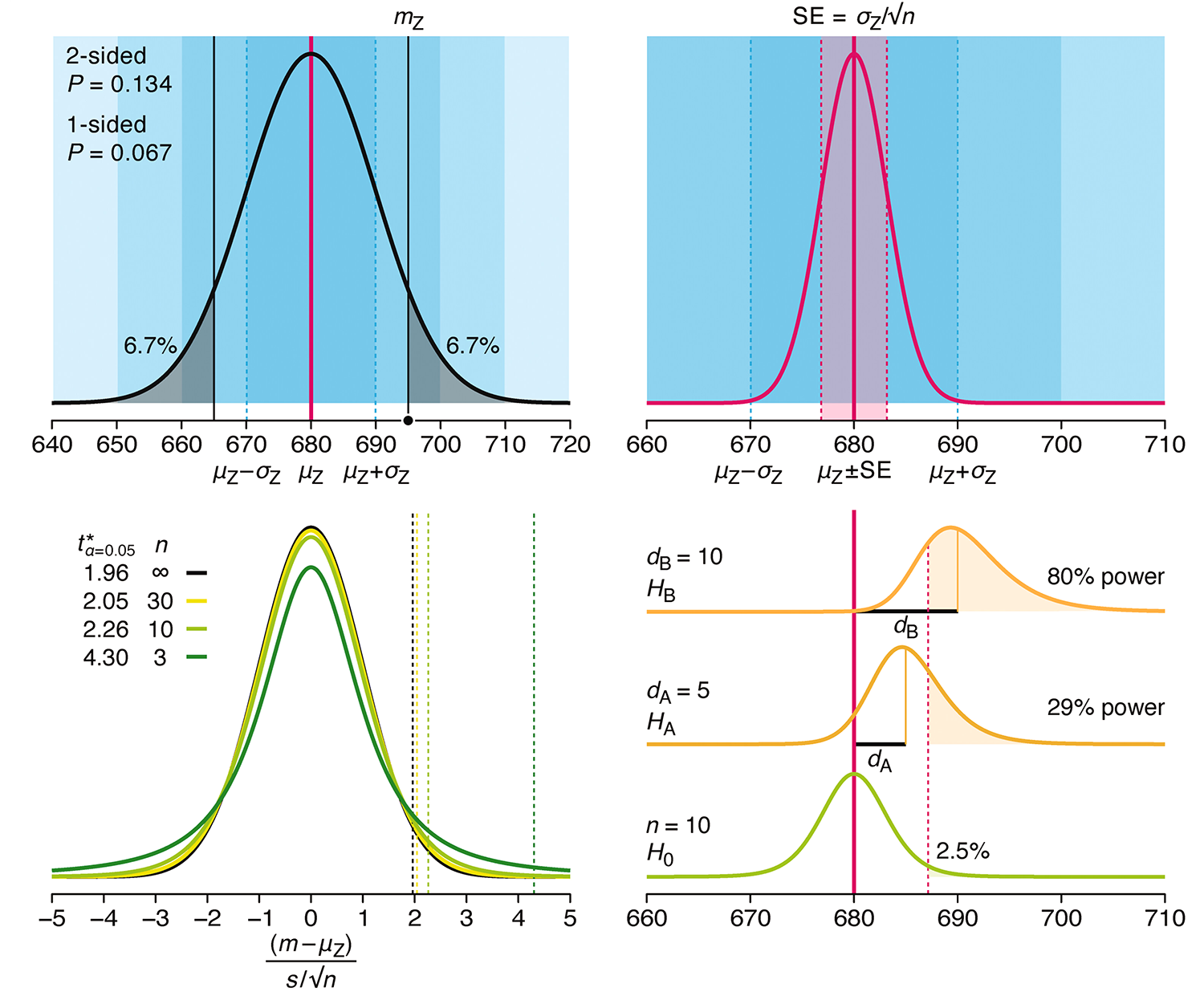
Understanding p-values and significance
P-values combined with estimates of effect size are used to assess the importance of experimental results. However, their interpretation can be invalidated by selection bias when testing multiple hypotheses, fitting multiple models or even informally selecting results that seem interesting after observing the data.
We offer an introduction to principled uses of p-values (targeted at the non-specialist) and identify questionable practices to be avoided.
Altman, N. & Krzywinski, M. (2024) Understanding p-values and significance. Laboratory Animals 58:443–446.

